Channel character of uncoupling protein-mediated transport
- PMID: 20206627
- PMCID: PMC3617986
- DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.02.068
Channel character of uncoupling protein-mediated transport
Abstract
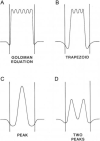
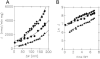
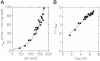
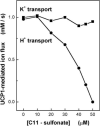
Mitochondrial uncoupling proteins (UCPs) are pure anion uniporters, which mediate fatty acid (FA) uniport leading to FA cycling. Protonated FAs then flip-flop back across the lipid bilayer. An existence of pure proton channel in UCPs is excluded by the equivalent flux-voltage dependencies for uniport of FAs and halide anions, which are best described by the Eyring barrier variant with a single energy well in the middle of two peaks. Experiments with FAs unable to flip and alkylsulfonates also support this view. Phylogenetically, UCPs took advantage of the common FA-uncoupling function of SLC25 family carriers and dropped their solute transport function.
Copyright 2010 Federation of European Biochemical Societies. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Hanák P, Ježek P. Mitochondrial uncoupling proteins and phylogenesis-UCP4 as the ancestral uncoupling protein. FEBS Lett. 2001;495:137–41. - PubMed
-
- Ježek P, Ježek J. Sequence anatomy of mitochondrial anion carriers. FEBS Lett. 2003;534:15–25. - PubMed
-
- Ježek P, Žáčka M, Růžička M, Škobisová E, Jabůrek M. Mitochondrial uncoupling proteins – facts and fantasies. Physiol. Res. 2004;53(S1):S199–S211. - PubMed
-
- Ježek P, Engstová H, Žáčková M, Vercesi AE, Costa ADT, Arruda P, Garlid KD. Fatty acid cycling mechanism and mitochondrial uncoupling proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1998;1365:319–27. - PubMed
-
- Ježek P. Fatty acid interaction with mitochondrial uncoupling proteins. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 1999;31:457–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

