Conformational dynamics of the Escherichia coli DNA polymerase manager proteins UmuD and UmuD'
- PMID: 20206636
- PMCID: PMC2853235
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.02.040
Conformational dynamics of the Escherichia coli DNA polymerase manager proteins UmuD and UmuD'
Abstract
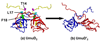
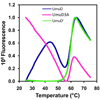
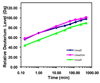
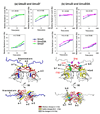
The expression of Escherichia coli umuD gene products is upregulated as part of the SOS response to DNA damage. UmuD is initially produced as a 139-amino-acid protein, which subsequently cleaves off its N-terminal 24 amino acids in a reaction dependent on RecA/single-stranded DNA, giving UmuD'. The two forms of the umuD gene products play different roles in the cell. UmuD is implicated in a primitive DNA damage checkpoint and prevents DNA polymerase IV-dependent -1 frameshift mutagenesis, while the cleaved form facilitates UmuC-dependent mutagenesis via formation of DNA polymerase V (UmuD'(2)C). Thus, the cleavage of UmuD is a crucial switch that regulates replication and mutagenesis via numerous protein-protein interactions. A UmuD variant, UmuD3A, which is noncleavable but is a partial biological mimic of the cleaved form UmuD', has been identified. We used hydrogen-deuterium exchange mass spectrometry (HXMS) to probe the conformations of UmuD, UmuD', and UmuD3A. In HXMS experiments, backbone amide hydrogens that are solvent accessible or not involved in hydrogen bonding become labeled with deuterium over time. Our HXMS results reveal that the N-terminal arm of UmuD, which is truncated in the cleaved form UmuD', is dynamic. Residues that are likely to contact the N-terminal arm show more deuterium exchange in UmuD' and UmuD3A than in UmuD. These observations suggest that noncleavable UmuD3A mimics the cleaved form UmuD' because, in both cases, the arms are relatively unbound from the globular domain. Gas-phase hydrogen exchange experiments, which specifically probe the exchange of side-chain hydrogens and are carried out on shorter timescales than solution experiments, show that UmuD' incorporates more deuterium than either UmuD or UmuD3A. This work indicates that these three forms of the UmuD gene products are highly flexible, which is of critical importance for their many protein interactions.
(c) 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The UmuD' protein filament and its potential role in damage induced mutagenesis.Structure. 1996 Dec 15;4(12):1401-12. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(96)00148-7. Structure. 1996. PMID: 8994967
-
Mutations affecting the ability of the Escherichia coli UmuD' protein to participate in SOS mutagenesis.J Bacteriol. 1999 Jan;181(1):177-85. doi: 10.1128/JB.181.1.177-185.1999. J Bacteriol. 1999. PMID: 9864328 Free PMC article.
-
Activity of the purified mutagenesis proteins UmuC, UmuD', and RecA in replicative bypass of an abasic DNA lesion by DNA polymerase III.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10777-81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10777. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992. PMID: 1438275 Free PMC article.
-
The "tale" of UmuD and its role in SOS mutagenesis.Bioessays. 2002 Feb;24(2):141-8. doi: 10.1002/bies.10040. Bioessays. 2002. PMID: 11835278 Review.
-
A new model for SOS-induced mutagenesis: how RecA protein activates DNA polymerase V.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2010 Jun;45(3):171-84. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2010.480968. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20441441 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ETD in a traveling wave ion guide at tuned Z-spray ion source conditions allows for site-specific hydrogen/deuterium exchange measurements.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2011 Oct;22(10):1784-93. doi: 10.1007/s13361-011-0196-7. Epub 2011 Jul 9. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2011. PMID: 21952892 Free PMC article.
-
Translesion DNA Synthesis.EcoSal Plus. 2012 Nov;5(1):10.1128/ecosalplus.7.2.2. doi: 10.1128/ecosalplus.7.2.2. EcoSal Plus. 2012. PMID: 26442823 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in protein structure monitored by use of gas-phase hydrogen/deuterium exchange.Proteomics. 2015 Aug;15(16):2842-50. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201400440. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Proteomics. 2015. PMID: 25603979 Free PMC article.
-
Altering the N-terminal arms of the polymerase manager protein UmuD modulates protein interactions.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 8;12(3):e0173388. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173388. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28273172 Free PMC article.
-
The entropic force generated by intrinsically disordered segments tunes protein function.Nature. 2018 Nov;563(7732):584-588. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0699-5. Epub 2018 Nov 12. Nature. 2018. PMID: 30420606 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Friedberg EC, Walker GC, Siede W, Wood RD, Schultz RA, Ellenberger T. DNA Repair and Mutagenesis. 2nd edit. Washington, DC: ASM Press; 2005.
-
- Friedberg EC. DNA damage and repair. Nature. 2003;421:436–440. - PubMed
-
- Simmons LA, Foti JJ, Cohen SE, Walker GC. Chapter 5.4.3. The SOS Regulatory Network. In: Bock A III, Kaper RC, Karp JB, C.Neidhardt PD, Nystrom F, Slauch T, Squires JM, CL, Ussary D, editors. EcoSal--Escherichia coli and Salmonella: cellular and molecular biology. Washington, D.C: ASM Press; 2008.
-
- Schlacher K, Goodman MF. Lessons from 50 years of SOS DNA-damage-induced mutagenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007;8:587–594. - PubMed
-
- Woodgate R, Sedgwick SG. Mutagenesis induced by bacterial UmuDC proteins and their plasmid homologues. Mol. Microbiol. 1992;6:2213–2218. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

