The PLC/IP 3 R/PKC pathway is required for ethanol-enhanced GABA release
- PMID: 20206640
- PMCID: PMC2849882
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.02.018
The PLC/IP 3 R/PKC pathway is required for ethanol-enhanced GABA release
Abstract
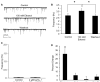
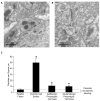
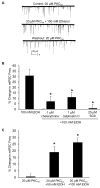
Research on the actions of ethanol at the GABAergic synapse has traditionally focused on postsynaptic mechanisms, but recent data demonstrate that ethanol also increases both evoked and spontaneous GABA release in many brain regions. Using whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings, we previously showed that ethanol increases spontaneous GABA release at the rat interneuron-Purkinje cell synapse. This presynaptic ethanol effect is dependent on calcium release from internal stores, possibly through activation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors (IP(3)Rs). After confirming that ethanol targets vesicular GABA release, in the present study we used electron microscopic immunohistochemistry to demonstrate that IP(3)Rs are located in presynaptic terminals of cerebellar interneurons. Activation of IP(3)Rs requires binding of IP(3), generated through activation of phospholipase C (PLC). We find that the PLC antagonist edelfosine prevents ethanol from increasing spontaneous GABA release. Diacylglycerol generated by PLC and calcium released by activation of the IP(3)R activate protein kinase C (PKC). Ethanol-enhanced GABA release was blocked by two PKC antagonists, chelerythrine and calphostin C. When a membrane impermeable PKC antagonist, PKC (19-36), was delivered intracellularly to the postsynaptic neuron, ethanol continued to increase spontaneous GABA release. Overall, these results suggest that activation of the PLC/IP(3)R/PKC pathway is necessary for ethanol to increase spontaneous GABA release from presynaptic terminals onto Purkinje cells.
(c) 2010. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Calcium release from presynaptic internal stores is required for ethanol to increase spontaneous gamma-aminobutyric acid release onto cerebellum Purkinje neurons.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007 Oct;323(1):356-64. doi: 10.1124/jpet.107.126144. Epub 2007 Jul 25. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007. PMID: 17652632
-
The role of protein kinase A in the ethanol-induced increase in spontaneous GABA release onto cerebellar Purkinje neurons.J Neurophysiol. 2008 Dec;100(6):3417-28. doi: 10.1152/jn.90970.2008. Epub 2008 Oct 22. J Neurophysiol. 2008. PMID: 18945815 Free PMC article.
-
Brain regional differences in the effect of ethanol on GABA release from presynaptic terminals.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008 Aug;326(2):596-603. doi: 10.1124/jpet.107.135418. Epub 2008 May 23. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008. PMID: 18502983 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol-enhanced GABA release: a focus on G protein-coupled receptors.Brain Res Rev. 2011 Jan 1;65(2):113-23. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2010.09.003. Epub 2010 Sep 15. Brain Res Rev. 2011. PMID: 20837058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The tipsy terminal: presynaptic effects of ethanol.Pharmacol Ther. 2005 Jul;107(1):80-98. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2005.01.006. Epub 2005 Apr 13. Pharmacol Ther. 2005. PMID: 15963352 Review.
Cited by
-
Brief alcohol exposure alters transcription in astrocytes via the heat shock pathway.Brain Behav. 2013 Mar;3(2):114-33. doi: 10.1002/brb3.125. Epub 2013 Feb 6. Brain Behav. 2013. PMID: 23533150 Free PMC article.
-
Mini-Review: Effects of Ethanol on GABAA Receptor-Mediated Neurotransmission in the Cerebellar Cortex--Recent Advances.Cerebellum. 2015 Aug;14(4):438-46. doi: 10.1007/s12311-014-0639-3. Cerebellum. 2015. PMID: 25575727 Review.
-
Effects of ethanol on glycinergic synaptic currents in mouse spinal cord neurons.J Neurophysiol. 2014 May;111(10):1940-8. doi: 10.1152/jn.00789.2013. Epub 2014 Feb 26. J Neurophysiol. 2014. PMID: 24572089 Free PMC article.
-
The Arabidopsis DREB2 genetic pathway is constitutively repressed by basal phosphoinositide-dependent phospholipase C coupled to diacylglycerol kinase.Front Plant Sci. 2013 Aug 8;4:307. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2013.00307. eCollection 2013. Front Plant Sci. 2013. PMID: 23964284 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Phospholipase C in GABAergic Inhibition and Its Relevance to Epilepsy.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 19;22(6):3149. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063149. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33808762 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baillieux H, De Smet HJ, Paquier PF, De Deyn PP, Marien P. Cerebellar neurocognition: insights into the bottom of the brain. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2008;110:763–773. - PubMed
-
- Bardo S, Cavazzini MG, Emptage N. The role of the endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ store in the plasticity of central neurons. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2006;27:78–84. - PubMed
-
- Bergmann J, Junghahn I, Brachwitz H, Langen P. Multiple effects of antitumor alkyl-lysophospholipid analogs on the cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration in a normal and a breast cancer cell line. Anticancer Res. 1994;14:1549–1556. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ, Bootman MD, Roderick HL. Calcium signalling: dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4:517–529. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

