An interdependent model of central/peripheral chemoreception: evidence and implications for ventilatory control
- PMID: 20206717
- PMCID: PMC2894288
- DOI: 10.1016/j.resp.2010.02.015
An interdependent model of central/peripheral chemoreception: evidence and implications for ventilatory control
Abstract
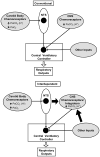
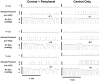
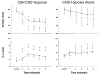
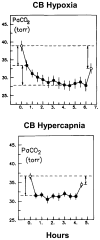
In this review we discuss the implications for ventilatory control of newer evidence suggesting that central and peripheral chemoreceptors are not functionally separate but rather that they are dependent upon one another such that the sensitivity of the medullary chemoreceptors is critically determined by input from the carotid body chemoreceptors and vice versa i.e., they are interdependent. We examine potential interactions of the interdependent central and carotid body (CB) chemoreceptors with other ventilatory-related inputs such as central hypoxia, lung stretch, and exercise. The limitations of current approaches addressing this question are discussed and future studies are suggested.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Peripheral chemoreceptors determine the respiratory sensitivity of central chemoreceptors to CO2 : role of carotid body CO2.J Physiol. 2015 Sep 15;593(18):4225-43. doi: 10.1113/JP270114. Epub 2015 Aug 16. J Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26171601 Free PMC article.
-
Plasticity of central chemoreceptors: effect of bilateral carotid body resection on central CO2 sensitivity.PLoS Med. 2007 Jul 24;4(7):e239. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0040239. PLoS Med. 2007. PMID: 17676946 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of chronic hypoxia upon chemoreception.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2007 Jul 1;157(1):154-61. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2007.01.009. Epub 2007 Jan 20. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2007. PMID: 17291837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Response time and sensitivity of the ventilatory response to CO2 in unanesthetized intact dogs: central vs. peripheral chemoreceptors.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2006 Jan;100(1):13-9. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00926.2005. Epub 2005 Sep 15. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2006. PMID: 16166236
-
Contributions of central and peripheral chemoreceptors to the ventilatory response to CO2/H+.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2010 Apr;108(4):989-94. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01059.2009. Epub 2010 Jan 14. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2010. PMID: 20075260 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The respiratory chemoreception conundrum: light at the end of the tunnel?Brain Res. 2013 May 20;1511:126-37. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.10.028. Epub 2012 Oct 23. Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23088963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Control of hyperpnoea and pulmonary gas exchange during prolonged exercise: The role of group III/IV muscle afferent feedback.J Physiol. 2024 Oct;602(20):5375-5389. doi: 10.1113/JP286993. Epub 2024 Sep 24. J Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39316014
-
Julius H. Comroe, Jr., distinguished lecture: central chemoreception: then ... and now.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2011 Jan;110(1):1-8. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01061.2010. Epub 2010 Nov 11. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2011. PMID: 21071595 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamate receptor plasticity in brainstem respiratory nuclei following chronic hypercapnia in goats.Physiol Rep. 2019 Apr;7(8):e14035. doi: 10.14814/phy2.14035. Physiol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30993898 Free PMC article.
-
CrossTalk proposal: a central hypoxia sensor contributes to the excitatory hypoxic ventilatory response.J Physiol. 2018 Aug;596(15):2935-2938. doi: 10.1113/JP275707. Epub 2018 Jun 27. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29947079 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Adams JM, Attinger FM, Attinger EO. Medullary and carotid chemoreceptor interaction for mild stimuli. Pflugers Arch. 1978;374:39–45. - PubMed
-
- Adams JM, Severns ML. Interaction of chemoreceptor effects and its dependence on the intensity of stimuli. J Appl Physiol. 1982;52:602–606. - PubMed
-
- Asmussen E, Nielsen M. Ventilatory responses to CO2 during work at normal and at low oxygen tensions. Acta Physiol Scand. 1957;39:27–35. - PubMed
-
- Badr MS, Skatrud JB, Dempsey JA. Determinants of poststimulus potentiation in humans during NREM sleep. J Appl Physiol. 1992;73:1958–1971. - PubMed
-
- Badr MS, Toiber F, Skatrud JB, Dempsey J. Pharyngeal narrowing/occlusion during central sleep apnea. J Appl Physiol. 1995;78:1806–1815. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

