Metformin therapy and outcomes in patients with advanced systolic heart failure and diabetes
- PMID: 20206893
- PMCID: PMC2855621
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2009.10.022
Metformin therapy and outcomes in patients with advanced systolic heart failure and diabetes
Abstract
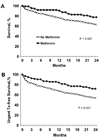
Background: Although 25% to 44% of patients with heart failure (HF) have diabetes mellitus (DM), the optimal treatment regimen for HF patients with DM is uncertain. We investigated the association between metformin therapy and outcomes in a cohort of advanced, systolic HF patients with DM.
Methods and results: Patients with DM and advanced, systolic HF (n = 401) were followed at a single university HF center between 1994 and 2008. The cohort was divided into 2 groups based on the presence or absence of metformin therapy. The cohort had a mean age of 56 +/- 11 years, left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of 24 +/- 7%, with 42% being New York Heart Association (NYHA) III and 45% NYHA IV. Twenty-five percent (n = 99) were treated with metformin therapy. The groups treated and not treated with metformin were similar in terms of age, sex, baseline LVEF, medical history, and baseline glycosylated hemoglobin. Metformin-treated patients had a higher body mass index, lower creatinine, and were less often on insulin. One-year survival in metformin-treated and non-metformin-treated patients was 91% and 76%, respectively (RR = 0.37, CI 0.18-0.76, P = .007). After multivariate adjustment for demographics, cardiac function, renal function, and HF medications, metformin therapy was associated with a nonsignificant trend for improved survival.
Conclusion: In patients with DM and advanced, systolic HF who are closely monitored, metformin therapy appears to be safe. Prospective studies are needed to determine whether metformin can improve HF outcome.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Metformin use in patients with diabetes mellitus and heart failure: friend or foe?J Card Fail. 2010 Mar;16(3):207-10. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2009.12.007. Epub 2010 Jan 18. J Card Fail. 2010. PMID: 20206894 No abstract available.
References
-
- MacDonald MR, Petrie MC, Hawkins NM, Petrie JR, Fisher M, McKelvie R, et al. Diabetes, left ventricular systolic dysfunction, and chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J. 2008;10:1224–1240. - PubMed
-
- Adams KF, Jr, Fonarow GC, Emerman CL, LeJemtel TH, Costanzo MR, Abraham WT, et al. Characteristics and outcomes of patients hospitalized for heart failure in the United States: rationale, design, and preliminary observations from the first 100,000 cases in the Acute Decompensated Heart Failure National Registry (ADHERE) Am Heart J. 2005;149:209–216. - PubMed
-
- Kannel WB, McGee DL. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease: the Framingham study. JAMA. 1979;241:2035–2038. - PubMed
-
- He J, Ogden LG, Bazzano LA, Vupputuri S, Loria C, Whelton PK. Risk factors for congestive heart failure in US men and women: NHANES I epidemiologic follow-up study. Arch Intern Med. 2001;161:996–1002. - PubMed
-
- Nichols GA, Gullion CM, Koro CE, Ephross SA, Brown JB. The incidence of congestive heart failure in type 2 diabetes: an update. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:1879–1884. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous