Oxime esters as selective, covalent inhibitors of the serine hydrolase retinoblastoma-binding protein 9 (RBBP9)
- PMID: 20207142
- PMCID: PMC2843764
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.02.011
Oxime esters as selective, covalent inhibitors of the serine hydrolase retinoblastoma-binding protein 9 (RBBP9)
Abstract
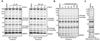
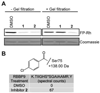
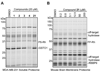
We recently described a fluorescence polarization platform for competitive activity-based protein profiling (fluopol-ABPP) that enables high-throughput inhibitor screening for enzymes with poorly characterized biochemical activity. Here, we report the discovery of a class of oxime ester inhibitors for the unannotated serine hydrolase RBBP9 from a full-deck (200,000+ compound) fluopol-ABPP screen conducted in collaboration with the Molecular Libraries Screening Center Network (MLSCN). We show that these compounds covalently inhibit RBBP9 by modifying enzyme's active site serine nucleophile and, based on competitive ABPP in cell and tissue proteomes, are selective for RBBP9 relative to other mammalian serine hydrolases.
2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human retinoblastoma binding protein 9, a serine hydrolase implicated in pancreatic cancers.Protein Pept Lett. 2012 Feb;19(2):194-7. doi: 10.2174/092986612799080356. Protein Pept Lett. 2012. PMID: 21933118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid development of a potent photo-triggered inhibitor of the serine hydrolase RBBP9.Chembiochem. 2012 Sep 24;13(14):2082-93. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201200445. Epub 2012 Aug 20. Chembiochem. 2012. PMID: 22907802 Free PMC article.
-
Chemoproteomic Identification of Serine Hydrolase RBBP9 as a Valacyclovir-Activating Enzyme.Mol Pharm. 2020 May 4;17(5):1706-1714. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.0c00131. Epub 2020 Mar 30. Mol Pharm. 2020. PMID: 32196348
-
Application of the RBBP9 Serine Hydrolase Inhibitor, ML114, Decouples Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Proliferation and Differentiation.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 26;21(23):8983. doi: 10.3390/ijms21238983. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33256189 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying inhibitors of ATM and ATR kinase activities.Methods Mol Med. 2003;85:49-56. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-380-1:49. Methods Mol Med. 2003. PMID: 12710196 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The metabolic serine hydrolases and their functions in mammalian physiology and disease.Chem Rev. 2011 Oct 12;111(10):6022-63. doi: 10.1021/cr200075y. Epub 2011 Jun 23. Chem Rev. 2011. PMID: 21696217 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Genome-wide siRNA screens identify RBBP9 function as a potential target in Fanconi anaemia-deficient head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma.Commun Biol. 2023 Jan 13;6(1):37. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-04389-3. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 36639418 Free PMC article.
-
Human retinoblastoma binding protein 9, a serine hydrolase implicated in pancreatic cancers.Protein Pept Lett. 2012 Feb;19(2):194-7. doi: 10.2174/092986612799080356. Protein Pept Lett. 2012. PMID: 21933118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fluorescence polarization assays in high-throughput screening and drug discovery: a review.Methods Appl Fluoresc. 2016 Apr 28;4(2):022001. doi: 10.1088/2050-6120/4/2/022001. Methods Appl Fluoresc. 2016. PMID: 28809163 Free PMC article.
-
The pharmacological landscape and therapeutic potential of serine hydrolases.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012 Jan 3;11(1):52-68. doi: 10.1038/nrd3620. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012. PMID: 22212679 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information

