From hematopoietic progenitors to B cells: mechanisms of lineage restriction and commitment
- PMID: 20207529
- PMCID: PMC2854230
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coi.2010.02.003
From hematopoietic progenitors to B cells: mechanisms of lineage restriction and commitment
Abstract
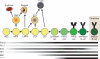
The generation of B lymphocytes from hematopoietic progenitors requires lineage-specific transcription factors that progressively direct cell fate choices. Differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells to lymphoid progenitors requires Ikaros-dependent lineage priming and graded levels of PU.1, which are controlled by Ikaros and Gfi1. E2A drives expression of EBF1, which initiates B lineage specification. EBF1, in addition to Pax5, is necessary for commitment to the B cell lineage. As a model of gene activation in early B lymphopoiesis, mb-1 genes are activated sequentially by factors (e.g. EBF1) that initiate chromatin modifications before transcription. This review highlights the requisite interplay between transcription factors and epigenetic mechanisms in the context of B cell development.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Hardy RR, Kincade PW, Dorshkind K. The protean nature of cells in the B lymphocyte lineage. Immunity. 2007;26:703–714. - PubMed
-
- Waddington CH. The epigenotype. Endeavour. 1942;1:18–20.
-
- Hu M, Krause D, Greaves M, Sharkis S, Dexter M, Heyworth C, Enver T. Multilineage gene expression precedes commitment in the hemopoietic system. Genes Dev. 1997;11:774–785. - PubMed
-
- Ye M, Iwasaki H, Laiosa CV, Stadfeld M, Xie H, Heck S, Clausen B, Akashi K, Graf T. Hematopoietic stem cells expressing the myeloid lysozyme gene retain long-term, multilineage repopulation potential. Immunity. 2003;19:689–699. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein B, Mikkelsen T, Xie X, Kamal M, Huebert D, Cuff J, Fry B, Meissner A, Wernig M, Plath K, et al. A bivalent chromatin structure marks key developmental genes in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2006;125:315–326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

