Role of the netrin-like domain of procollagen C-proteinase enhancer-1 in the control of metalloproteinase activity
- PMID: 20207734
- PMCID: PMC2871463
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.086447
Role of the netrin-like domain of procollagen C-proteinase enhancer-1 in the control of metalloproteinase activity
Abstract
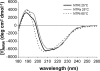
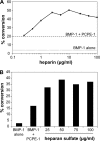
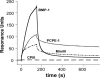
The netrin-like (NTR) domain is a feature of several extracellular proteins, most notably the N-terminal domain of tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs), where it functions as a strong inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases and some other members of the metzincin superfamily. The presence of a C-terminal NTR domain in procollagen C-proteinase enhancers (PCPEs), proteins that stimulate the activity of astacin-like tolloid proteinases, raises the possibility that this might also have inhibitory activity. Here we show that both long and short forms of the PCPE-1 NTR domain, the latter beginning at the N-terminal cysteine known to be critical for TIMP activity, show no inhibition, at micromolar concentrations, of several members of the metzincin superfamily, including matrix metalloproteinase-2, bone morphogenetic protein-1 (a tolloid proteinase), and different ADAMTS (a disintegrin and a metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs) proteinases from the adamalysin family. In contrast, we report that the NTR domain within PCPE-1 leads to superstimulation of bone morphogenetic protein-1 activity in the presence of heparin and heparan sulfate. These observations point to a new mechanism whereby binding to cell surface-associated or extracellular heparin-like sulfated glycosaminoglycans might provide a means to accelerate procollagen processing in specific cellular and extracellular microenvironments.
Figures

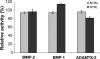



References
-
- Nagase H., Visse R., Murphy G. (2006) Cardiovasc. Res. 69, 562–573 - PubMed
-
- Stetefeld J., Jenny M., Schulthess T., Landwehr R., Schumacher B., Frank S., Rüegg M. A., Engel J., Kammerer R. A. (2001) Nat. Struct. Biol. 8, 705–709 - PubMed
-
- Bezakova G., Ruegg M. A. (2003) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4, 295–308 - PubMed
-
- Cirulli V., Yebra M. (2007) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8, 296–306 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

