Insulin-like growth factor-I-stimulated insulin receptor substrate-1 negatively regulates Src homology 2 domain-containing protein-tyrosine phosphatase substrate-1 function in vascular smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 20207740
- PMCID: PMC2871434
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.092270
Insulin-like growth factor-I-stimulated insulin receptor substrate-1 negatively regulates Src homology 2 domain-containing protein-tyrosine phosphatase substrate-1 function in vascular smooth muscle cells
Abstract
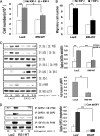
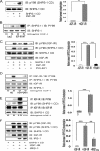
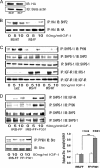
Vascular smooth muscle cells maintained in normal (5.6 mm) glucose respond to insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) with increased protein synthesis but do not proliferate. In contrast, hyperglycemia alters responsiveness to IGF-I, resulting in increased SHPS-1 phosphorylation and assembly of a signaling complex that enhances MAPK and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathways. Hyperglycemia also reduces the basal IRS-1 concentration and IGF-I-stimulated IRS-1-linked signaling. To determine if failure to down-regulate IRS-1 alters vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) responses to IGF-I, we overexpressed IRS-1 in VSMCs maintained in high glucose. These cultures showed reduced SHPS-1 phosphorylation, transfer of SHP-2 to SHPS-1, and impaired Shc and MAPK phosphorylation and cell proliferation in response to IGF-I. In vitro studies demonstrated that SHPS-1 was a substrate for type I IGF receptor (IGF-IR) and that IRS-1 competitively inhibited SHPS-1 phosphorylation. Exposure of VSMC cultures to a peptide that inhibited IRS-1/IGF-IR interaction showed that IRS-1 binding to IGF-IR impairs SHPS-1 phosphorylation in vivo. IRS-1 also sequestered SHP-2. Expression of an IRS-1 mutant (Y1179F/Y1229F) reduced IRS-1/SHP-2 association, and exposure of cells expressing the mutant to the inhibitory peptide enhanced SHPS-1 phosphorylation and SHP-2 transfer. This result was confirmed by expressing an IRS-1 mutant that had both impaired binding to IGF-IR and to SHP-2 IGF-I increased SHPS-1 phosphorylation, SHP-2 association with SHPS-1, Shc MAPK phosphorylation, and proliferation in cells expressing the mutant. We conclude that IRS-1 is an important factor for maintaining VSMCs in the non-proliferative state and that its down-regulation is a component of the VSMC response to hyperglycemic stress that results in an enhanced response to IGF-I.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Role of SHPS-1 in the regulation of insulin-like growth factor I-stimulated Shc and mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in vascular smooth muscle cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Jul;16(7):3353-64. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-10-0918. Epub 2005 May 11. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15888547 Free PMC article.
-
The association between integrin-associated protein and SHPS-1 regulates insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2003 Sep;14(9):3519-28. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e03-04-0239. Epub 2003 May 29. Mol Biol Cell. 2003. PMID: 12972543 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Src kinase in insulin-like growth factor-dependent mitogenic signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells.J Biol Chem. 2006 Sep 1;281(35):25041-53. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M602866200. Epub 2006 Jul 5. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16825188
-
Interaction between insulin-like growth factor-I receptor and alphaVbeta3 integrin linked signaling pathways: cellular responses to changes in multiple signaling inputs.Mol Endocrinol. 2005 Jan;19(1):1-11. doi: 10.1210/me.2004-0376. Epub 2004 Nov 4. Mol Endocrinol. 2005. PMID: 15528274 Review.
-
Role of the integrin alphaVbeta3 in mediating increased smooth muscle cell responsiveness to IGF-I in response to hyperglycemic stress.Growth Horm IGF Res. 2007 Aug;17(4):265-70. doi: 10.1016/j.ghir.2007.01.004. Epub 2007 Apr 6. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2007. PMID: 17412627 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PDK1 recruitment to the SHPS-1 signaling complex enhances insulin-like growth factor-i-stimulated AKT activation and vascular smooth muscle cell survival.J Biol Chem. 2010 Sep 17;285(38):29416-24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.155325. Epub 2010 Jul 19. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20643654 Free PMC article.
-
IGF-I stimulates cooperative interaction between the IGF-I receptor and CSK homologous kinase that regulates SHPS-1 phosphorylation in vascular smooth muscle cells.Mol Endocrinol. 2011 Sep;25(9):1636-49. doi: 10.1210/me.2011-0035. Epub 2011 Jul 28. Mol Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21799000 Free PMC article.
-
Aldosterone enhances IGF-I-mediated signaling and biological function in vascular smooth muscle cells.Endocrinology. 2010 Dec;151(12):5851-64. doi: 10.1210/en.2010-0350. Epub 2010 Sep 29. Endocrinology. 2010. PMID: 20881255 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Aberrant IGF-I Signaling in Diabetic Male Rat Retina Prevents and Reverses Changes of Diabetic Retinopathy.J Diabetes Res. 2019 Mar 27;2019:6456032. doi: 10.1155/2019/6456032. eCollection 2019. J Diabetes Res. 2019. PMID: 31049357 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperglycemia induces vascular smooth muscle cell dedifferentiation by suppressing insulin receptor substrate-1-mediated p53/KLF4 complex stabilization.J Biol Chem. 2019 Feb 15;294(7):2407-2421. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005398. Epub 2018 Dec 21. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30578299 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Imai Y., Clemmons D. R. (1999) Endocrinology 140, 4228–4235 - PubMed
-
- Myers M. G., Jr., Sun X. J., Cheatham B., Jachna B. R., Glasheen E. M., Backer J. M., White M. F. (1993) Endocrinology 132, 1421–1430 - PubMed
-
- Sun X. J., Rothenberg P., Kahn C. R., Backer J. M., Araki E., Wilden P. A., Cahill D. A., Goldstein B. J., White M. F. (1991) Nature 352, 73–77 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

