Variance component model to account for sample structure in genome-wide association studies
- PMID: 20208533
- PMCID: PMC3092069
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.548
Variance component model to account for sample structure in genome-wide association studies
Abstract
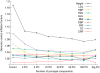
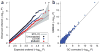
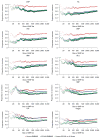
Although genome-wide association studies (GWASs) have identified numerous loci associated with complex traits, imprecise modeling of the genetic relatedness within study samples may cause substantial inflation of test statistics and possibly spurious associations. Variance component approaches, such as efficient mixed-model association (EMMA), can correct for a wide range of sample structures by explicitly accounting for pairwise relatedness between individuals, using high-density markers to model the phenotype distribution; but such approaches are computationally impractical. We report here a variance component approach implemented in publicly available software, EMMA eXpedited (EMMAX), that reduces the computational time for analyzing large GWAS data sets from years to hours. We apply this method to two human GWAS data sets, performing association analysis for ten quantitative traits from the Northern Finland Birth Cohort and seven common diseases from the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium. We find that EMMAX outperforms both principal component analysis and genomic control in correcting for sample structure.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
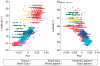

References
-
- Weir BS, Anderson AD, Hepler AB. Genetic relatedness analysis: modern data and new challenges. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7:771–780. - PubMed
-
- Helgason A, Yngvadttir B, Hrafnkelsson B, Gulcher J, Stefnsson K. An Icelandic example of the impact of population structure on association studies. Nat Genet. 2005;37:90–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 5PL1NS062410-03/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087679/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- NH084698/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- 1K25HL080079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5RL1MH083268-03/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 5UL1DE019580-03/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- RL1 MH083268/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM053275/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 1MH083268/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HL087679-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DA024417/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 DE019580/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- 6R01HL087679-03/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K25 HL080079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- GM053275-14/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA024417/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 ES045530/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- PL1 NS062410/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

