Programmed death-1-induced interleukin-10 production by monocytes impairs CD4+ T cell activation during HIV infection
- PMID: 20208540
- PMCID: PMC4229134
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.2106
Programmed death-1-induced interleukin-10 production by monocytes impairs CD4+ T cell activation during HIV infection
Abstract
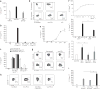
Viral replication and microbial translocation from the gut to the blood during HIV infection lead to hyperimmune activation, which contributes to the decline in CD4+ T cell numbers during HIV infection. Programmed death-1 (PD-1) and interleukin-10 (IL-10) are both upregulated during HIV infection. Blocking interactions between PD-1 and programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) and between IL-10 and IL-10 receptor (IL-10R) results in viral clearance and improves T cell function in animal models of chronic viral infections. Here we show that high amounts of microbial products and inflammatory cytokines in the plasma of HIV-infected subjects lead to upregulation of PD-1 expression on monocytes that correlates with high plasma concentrations of IL-10. Triggering of PD-1 expressed on monocytes by PD-L1 expressed on various cell types induced IL-10 production and led to reversible CD4+ T cell dysfunction. We describe a new function for PD-1 whereby microbial products inhibit T cell expansion and function by upregulating PD-1 levels and IL-10 production by monocytes after binding of PD-1 by PD-L1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


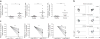

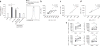
References
-
- El-Far M, et al. T-cell exhaustion in HIV infection. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2008;5:13–19. - PubMed
-
- Klenerman P, Hill A. T cells and viral persistence: lessons from diverse infections. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:873–879. - PubMed
-
- Brenchley JM, et al. Microbial translocation is a cause of systemic immune activation in chronic HIV infection. Nat Med. 2006;12:1365–1371. - PubMed
-
- Breen EC, et al. Infection with HIV is associated with elevated IL-6 levels and production. J Immunol. 1990;144:480–484. - PubMed
-
- Chollet-Martin S, et al. Comparison of plasma cytokine levels in African patients with HIV-1 and HIV-2 infection. AIDS. 1994;8:879–884. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

