FOXM1 is a transcriptional target of ERalpha and has a critical role in breast cancer endocrine sensitivity and resistance
- PMID: 20208560
- PMCID: PMC2874720
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2010.47
FOXM1 is a transcriptional target of ERalpha and has a critical role in breast cancer endocrine sensitivity and resistance
Abstract
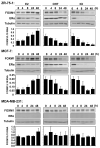
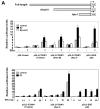
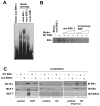
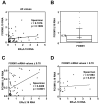
In this study, we investigated the regulation of FOXM1 expression by estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) and its role in hormonal therapy and endocrine resistance. FOXM1 protein and mRNA expression was regulated by ER-ligands, including estrogen, tamoxifen (OHT) and fulvestrant (ICI182780; ICI) in breast carcinoma cell lines. Depletion of ERalpha by RNA interference (RNAi) in MCF-7 cells downregulated FOXM1 expression. Reporter gene assays showed that ERalpha activates FOXM1 transcription through an estrogen-response element (ERE) located within the proximal promoter region. The direct binding of ERalpha to the FOXM1 promoter was confirmed in vitro by mobility shift and DNA pull-down assays and in vivo by chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analysis. Our data also revealed that upon OHT treatment ERalpha recruits histone deacetylases to the ERE site of the FOXM1 promoter, which is associated with a decrease in histone acetylation and transcription activity. Importantly, silencing of FOXM1 by RNAi abolished estrogen-induced MCF-7 cell proliferation and overcame acquired tamoxifen resistance. Conversely, ectopic expression of FOXM1 abrogated the cell cycle arrest mediated by the anti-estrogen OHT. OHT repressed FOXM1 expression in endocrine sensitive but not resistant breast carcinoma cell lines. Furthermore, qRT-PCR analysis of breast cancer patient samples revealed that there was a strong and significant positive correlation between ERalpha and FOXM1 mRNA expression. Collectively, these results show FOXM1 to be a key mediator of the mitogenic functions of ERalpha and estrogen in breast cancer cells, and also suggest that the deregulation of FOXM1 may contribute to anti-estrogen insensitivity.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The Forkhead box M1 protein regulates the transcription of the estrogen receptor alpha in breast cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 2006 Sep 1;281(35):25167-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M603906200. Epub 2006 Jun 28. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16809346
-
Endocrine therapy resistance can be associated with high estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) expression and reduced ERalpha phosphorylation in breast cancer models.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2006 Dec;13(4):1121-33. doi: 10.1677/erc.1.01257. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2006. PMID: 17158758
-
ERβ1 represses FOXM1 expression through targeting ERα to control cell proliferation in breast cancer.Am J Pathol. 2011 Sep;179(3):1148-56. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.05.052. Epub 2011 Jul 16. Am J Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21763263 Free PMC article.
-
FOXM1: From cancer initiation to progression and treatment.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jan;1819(1):28-37. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.09.004. Epub 2011 Sep 29. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 21978825 Review.
-
Insights into a Critical Role of the FOXO3a-FOXM1 Axis in DNA Damage Response and Genotoxic Drug Resistance.Curr Drug Targets. 2016;17(2):164-77. doi: 10.2174/1389450115666141122211549. Curr Drug Targets. 2016. PMID: 25418858 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Critical Roles of SRC-3 in the Development and Progression of Breast Cancer, Rendering It a Prospective Clinical Target.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 31;15(21):5242. doi: 10.3390/cancers15215242. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37958417 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogen receptor coregulators and pioneer factors: the orchestrators of mammary gland cell fate and development.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2014 Aug 12;2:34. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2014.00034. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 25364741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic genes of breast cancer revealed by gene co-expression network analysis.Oncol Lett. 2017 Oct;14(4):4535-4542. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6779. Epub 2017 Aug 21. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 29085450 Free PMC article.
-
Forkhead box proteins: tuning forks for transcriptional harmony.Nat Rev Cancer. 2013 Jul;13(7):482-95. doi: 10.1038/nrc3539. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23792361 Review.
-
FoxO3a Inhibits Tamoxifen-Resistant Breast Cancer Progression by Inducing Integrin α5 Expression.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 2;14(1):214. doi: 10.3390/cancers14010214. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35008379 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ali S, Coombes RC. Endocrine-responsive breast cancer and strategies for combating resistance. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:101–12. - PubMed
-
- Bourdeau V, Deschenes J, Metivier R, Nagai Y, Nguyen D, Bretschneider N, et al. Genome-wide identification of high-affinity estrogen response elements in human and mouse. Mol Endocrinol. 2004;18:1411–27. - PubMed
-
- Brunner N, Zugmaier G, Bano M, Ennis BW, Clarke R, Cullen KJ, et al. Endocrine therapy of human breast cancer cells: the role of secreted polypeptide growth factors. Cancer Cells. 1989;1:81–6. - PubMed
-
- Butt AJ, McNeil CM, Musgrove EA, Sutherland RL. Downstream targets of growth factor and oestrogen signalling and endocrine resistance: the potential roles of c-Myc, cyclin D1 and cyclin E. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005;12(Suppl 1):S47–59. - PubMed
-
- Carroll JS, Brown M. Estrogen receptor target gene: an evolving concept. Mol Endocrinol. 2006;20:1707–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

