Integrated Microfluidic Reactors
- PMID: 20209065
- PMCID: PMC2832182
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nantod.2009.10.007
Integrated Microfluidic Reactors
Abstract
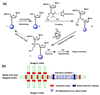
Microfluidic reactors exhibit intrinsic advantages of reduced chemical consumption, safety, high surface-area-to-volume ratios, and improved control over mass and heat transfer superior to the macroscopic reaction setting. In contract to a continuous-flow microfluidic system composed of only a microchannel network, an integrated microfluidic system represents a scalable integration of a microchannel network with functional microfluidic modules, thus enabling the execution and automation of complicated chemical reactions in a single device. In this review, we summarize recent progresses on the development of integrated microfluidics-based chemical reactors for (i) parallel screening of in situ click chemistry libraries, (ii) multistep synthesis of radiolabeled imaging probes for positron emission tomography (PET), (iii) sequential preparation of individually addressable conducting polymer nanowire (CPNW), and (iv) solid-phase synthesis of DNA oligonucleotides. These proof-of-principle demonstrations validate the feasibility and set a solid foundation for exploring a broad application of the integrated microfluidic system.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Multistep synthesis of a radiolabeled imaging probe using integrated microfluidics.Science. 2005 Dec 16;310(5755):1793-6. doi: 10.1126/science.1118919. Science. 2005. PMID: 16357255
-
Controllable synthesis of nanocrystals in droplet reactors.Lab Chip. 2017 Dec 19;18(1):41-56. doi: 10.1039/c7lc00800g. Lab Chip. 2017. PMID: 29098217 Review.
-
An integrated microfluidic device for large-scale in situ click chemistry screening.Lab Chip. 2009 Aug 21;9(16):2281-5. doi: 10.1039/b907430a. Epub 2009 Jun 17. Lab Chip. 2009. PMID: 19636457 Free PMC article.
-
Microfluidics for positron emission tomography probe development.Mol Imaging. 2010 Aug;9(4):175-91. Mol Imaging. 2010. PMID: 20643021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An integrated microfluidic chip enabling control and spatially resolved monitoring of temperature in micro flow reactors.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015 Jan;407(2):387-96. doi: 10.1007/s00216-014-8297-3. Epub 2014 Nov 7. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015. PMID: 25377779
Cited by
-
The development of a general strategy for the synthesis of tyramine-based natural products by using continuous flow techniques.Chemistry. 2010 Nov 15;16(43):12797-800. doi: 10.1002/chem.201002102. Chemistry. 2010. PMID: 20931578 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Microfluidic Hydrodynamic Focusing for Synthesis of Nanomaterials.Nano Today. 2016 Dec;11(6):778-792. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2016.10.006. Epub 2016 Nov 12. Nano Today. 2016. PMID: 30337950 Free PMC article.
-
An FEP Microfluidic Reactor for Photochemical Reactions.Micromachines (Basel). 2018 Mar 30;9(4):156. doi: 10.3390/mi9040156. Micromachines (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30424090 Free PMC article.
-
A flow-microreactor approach to protecting-group-free synthesis using organolithium compounds.Nat Commun. 2011;2:264. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1264. Nat Commun. 2011. PMID: 21468016
-
Microfluidic devices: useful tools for bioprocess intensification.Molecules. 2011 Sep 30;16(10):8368-401. doi: 10.3390/molecules16108368. Molecules. 2011. PMID: 21963626 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Smith M, March J. March's advanced organic chemistry, reactions, mechanisms, and structure. 6th ed. Hoboken: Wiley-Interscience; 2007.
-
- Li JJ. Name Reactions A Collection of Detailed Reaction Mechanisms. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg; 2006.
-
- Nicolaou KC, Sorensen EJ. Classics in total synthesis : targets, strategies, methods. New York: VCH; 1996.
-
- Balzani V, Credi A, Raymo FM, Stoddart JF. Angew. Chemie. Int. Ed. 2000;39:3349. - PubMed
-
- Whitesides GM. Nature. 2006;442:368. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
