Phylogenomic analyses reveal the evolutionary origin of the inhibin alpha-subunit, a unique TGFbeta superfamily antagonist
- PMID: 20209104
- PMCID: PMC2832003
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009457
Phylogenomic analyses reveal the evolutionary origin of the inhibin alpha-subunit, a unique TGFbeta superfamily antagonist
Abstract
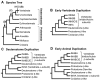
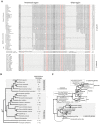
Transforming growth factor-beta (TGFbeta) homologues form a diverse superfamily that arose early in animal evolution and control cellular function through membrane-spanning, conserved serine-threonine kinases (RII and RI receptors). Activin and inhibin are related dimers within the TGFbeta superfamily that share a common beta-subunit. The evolution of the inhibin alpha-subunit created the only antagonist within the TGFbeta superfamily and the only member known to act as an endocrine hormone. This hormone introduced a new level of complexity and control to vertebrate reproductive function. The novel functions of the inhibin alpha-subunit appear to reflect specific insertion-deletion changes within the inhibin beta-subunit that occurred during evolution. Using phylogenomic analysis, we correlated specific insertions with the acquisition of distinct functions that underlie the phenotypic complexity of vertebrate reproductive processes. This phylogenomic approach presents a new way of understanding the structure-function relationships between inhibin, activin, and the larger TGFbeta superfamily.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transforming growth factor-beta modulates inhibin A bioactivity in the LbetaT2 gonadotrope cell line by competing for binding to betaglycan.Mol Endocrinol. 2002 Dec;16(12):2754-63. doi: 10.1210/me.2002-0014. Mol Endocrinol. 2002. PMID: 12456797
-
A common biosynthetic pathway governs the dimerization and secretion of inhibin and related transforming growth factor beta (TGFbeta) ligands.J Biol Chem. 2009 Apr 3;284(14):9311-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M808763200. Epub 2009 Feb 3. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19193648 Free PMC article.
-
Follicle-restricted compartmentalization of transforming growth factor beta superfamily ligands in the feline ovary.Biol Reprod. 2004 Mar;70(3):846-59. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.103.021857. Epub 2003 Dec 3. Biol Reprod. 2004. PMID: 14656728
-
Molecular biology of inhibin action.Semin Reprod Med. 2004 Aug;22(3):269-76. doi: 10.1055/s-2004-831902. Semin Reprod Med. 2004. PMID: 15319829 Review.
-
Pituitary actions of ligands of the TGF-beta family: activins and inhibins.Reproduction. 2006 Aug;132(2):207-15. doi: 10.1530/rep.1.01073. Reproduction. 2006. PMID: 16885530 Review.
Cited by
-
Activins and Inhibins: Roles in Development, Physiology, and Disease.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2016 Jul 1;8(7):a021881. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a021881. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2016. PMID: 27328872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibin α-subunit N terminus interacts with activin type IB receptor to disrupt activin signaling.J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 9;287(11):8060-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.293381. Epub 2012 Jan 20. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22267736 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-β Ligand Cross-Subfamily Interactions in the Response of Caenorhabditis elegans to Bacterial Pathogens.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Aug 9:2023.05.05.539606. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.05.539606. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: PLoS Genet. 2024 Jun 14;20(6):e1011324. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011324. PMID: 37215035 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Virtual High-Throughput Screening To Identify Novel Activin Antagonists.J Med Chem. 2015 Jul 23;58(14):5637-48. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00753. Epub 2015 Jul 7. J Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 26098096 Free PMC article.
-
Follistatin Forms a Stable Complex With Inhibin A That Does Not Interfere With Activin A Antagonism.Endocrinology. 2023 Jan 9;164(3):bqad017. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqad017. Endocrinology. 2023. PMID: 36718082 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu MY, Hill CS. Tgf-beta superfamily signaling in embryonic development and homeostasis. Dev Cell. 2009;16:329–343. - PubMed
-
- Feng XH, Derynck R. Specificity and versatility in tgf-beta signaling through Smads. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2005;21:659–693. - PubMed
-
- Massagué J. TGF-beta signal transduction. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:753–791. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

