Infection in systemic lupus erythematosus: friend or foe?
- PMID: 20209114
- PMCID: PMC2830655
- DOI: 10.2217/ijr.09.72
Infection in systemic lupus erythematosus: friend or foe?
Abstract
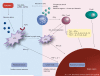
Infectious agents have long been implicated in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Common viruses, such as the Epstein-Barr virus, transfusion transmitted virus, parvovirus and cytomegalovirus, have an increased prevalence in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. They may contribute to disease pathogenesis through triggering autoimmunity via structural or functional molecular mimicry, encoding proteins that induce cross-reactive immune responses to self antigens or modulate antigen processing, activation, or apoptosis of B and T cells, macrophages or dendritic cells. Alternatively, some infectious agents, such as malaria, Toxoplasma gondii and Helicobacter pylori, may have a protective effect. Vaccinations may play dual roles by protecting against friend and foe alike.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The cryptic interplay between systemic lupus erythematosus and infections.Autoimmun Rev. 2014 Feb;13(2):96-102. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2013.09.004. Epub 2013 Sep 17. Autoimmun Rev. 2014. PMID: 24051103 Review.
-
Viral Infections and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: New Players in an Old Story.Viruses. 2021 Feb 11;13(2):277. doi: 10.3390/v13020277. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33670195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current mechanistic insights into the role of infection in systemic lupus erythematosus.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Sep;117:109122. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109122. Epub 2019 Jun 18. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31226637 Review.
-
Epstein-Barr virus and systemic lupus erythematosus.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2006 Sep;18(5):462-7. doi: 10.1097/01.bor.0000240355.37927.94. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2006. PMID: 16896283 Review.
-
Epstein-Barr Functional Mimicry: Pathogenicity of Oncogenic Latent Membrane Protein-1 in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Autoimmunity.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 3;11:606936. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.606936. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33613527 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Role of Helicobacter pylori infection in autoimmune diseases.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2012 Jul;24(4):429-34. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0b013e3283542d0b. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2012. PMID: 22617822 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progressive respiratory distress in a 42-year-old HIV-positive woman with systemic lupus erythematosus.Eur J Med Res. 2017 Jun 17;22(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s40001-017-0261-1. Eur J Med Res. 2017. PMID: 28623951 Free PMC article.
-
Toxoplasmosis and Polygenic Disease Susceptibility Genes: Extensive Toxoplasma gondii Host/Pathogen Interactome Enrichment in Nine Psychiatric or Neurological Disorders.J Pathog. 2013;2013:965046. doi: 10.1155/2013/965046. Epub 2013 Mar 4. J Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23533776 Free PMC article.
-
Lupus and Epstein-Barr.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2012 Jul;24(4):383-8. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0b013e3283535801. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2012. PMID: 22504579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intestinal dysbiosis associated with systemic lupus erythematosus.mBio. 2014 Sep 30;5(5):e01548-14. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01548-14. mBio. 2014. PMID: 25271284 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
