Bacillus thuringiensis Cry5B protein is highly efficacious as a single-dose therapy against an intestinal roundworm infection in mice
- PMID: 20209154
- PMCID: PMC2830470
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000614
Bacillus thuringiensis Cry5B protein is highly efficacious as a single-dose therapy against an intestinal roundworm infection in mice
Abstract
Background: Intestinal parasitic nematode diseases are one of the great diseases of our time. Intestinal roundworm parasites, including hookworms, whipworms, and Ascaris, infect well over 1 billion people and cause significant morbidity, especially in children and pregnant women. To date, there is only one drug, albendazole, with adequate efficacy against these parasites to be used in mass drug administration, although tribendimidine may emerge as a second. Given the hundreds of millions of people to be treated, the threat of parasite resistance, and the inadequacy of current treatments, new anthelmintics are urgently needed. Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) crystal (Cry) proteins are the most common used biologically produced insecticides in the world and are considered non-toxic to vertebrates.
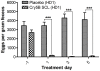
Methods/principal findings: Here we study the ability of a nematicidal Cry protein, Cry5B, to effect a cure in mice of a chronic roundworm infection caused by the natural intestinal parasite, Heligmosomoides bakeri (formerly polygyrus). We show that Cry5B produced from either of two Bt strains can act as an anthelmintic in vivo when administered as a single dose, achieving a approximately 98% reduction in parasite egg production and approximately 70% reduction in worm burdens when delivered per os at approximately 700 nmoles/kg (90-100 mg/kg). Furthermore, our data, combined with the findings of others, suggest that the relative efficacy of Cry5B is either comparable or superior to current anthelmintics. We also demonstrate that Cry5B is likely to be degraded quite rapidly in the stomach, suggesting that the actual dose reaching the parasites is very small.
Conclusions/significance: This study indicates that Bt Cry proteins such as Cry5B have excellent anthelmintic properties in vivo and that proper formulation of the protein is likely to reveal a superior anthelmintic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Bacillus thuringiensis Cry5B protein as a new pan-hookworm cure.Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2018 Aug;8(2):287-294. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2018.05.001. Epub 2018 May 4. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2018. PMID: 29772478 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo and in vitro studies of Cry5B and nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist anthelmintics reveal a powerful and unique combination therapy against intestinal nematode parasites.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018 May 18;12(5):e0006506. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006506. eCollection 2018 May. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018. PMID: 29775454 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic and single-dose in vivo therapeutic studies of Cry5B anthelmintic action against hookworms.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012;6(11):e1900. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001900. Epub 2012 Nov 8. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012. PMID: 23145203 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial pore-forming proteins as anthelmintics.Invert Neurosci. 2012 Jun;12(1):37-41. doi: 10.1007/s10158-012-0135-8. Epub 2012 May 5. Invert Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22562659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An overview of the safety and biological effects of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry toxins in mammals.J Appl Toxicol. 2016 May;36(5):630-48. doi: 10.1002/jat.3252. Epub 2015 Nov 4. J Appl Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 26537666 Review.
Cited by
-
Transposon-mediated chromosomal integration of transgenes in the parasitic nematode Strongyloides ratti and establishment of stable transgenic lines.PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(8):e1002871. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002871. Epub 2012 Aug 9. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 22912584 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and glycolipid binding properties of the nematicidal protein Cry5B.Biochemistry. 2012 Dec 11;51(49):9911-21. doi: 10.1021/bi301386q. Epub 2012 Nov 26. Biochemistry. 2012. PMID: 23150986 Free PMC article.
-
Diethylcarbamazine, TRP channels and Ca2+ signaling in cells of the Ascaris intestine.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 9;12(1):21317. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-25648-7. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36494409 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillus thuringiensis Cry5B protein as a new pan-hookworm cure.Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2018 Aug;8(2):287-294. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2018.05.001. Epub 2018 May 4. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2018. PMID: 29772478 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant Paraprobiotics as a New Paradigm for Treating Gastrointestinal Nematode Parasites of Humans.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021 Feb 17;65(3):e01469-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01469-20. Print 2021 Feb 17. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021. PMID: 33318013 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hotez PJ, Kamath A. Neglected tropical diseases in sub-saharan Africa: review of their prevalence, distribution, and disease burden. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2009;3:e412. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000412. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hotez PJ, Molyneux DH, Fenwick A, Kumaresan J, Sachs SE, et al. Control of neglected tropical diseases. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:1018–1027. - PubMed
-
- Bethony J, Brooker S, Albonico M, Geiger SM, Loukas A, et al. Soil-transmitted helminth infections: ascariasis, trichuriasis, and hookworm. Lancet. 2006;367:1521–1532. - PubMed
-
- Cooper PJ, Chico ME, Losonsky G, Sandoval C, Espinel I, et al. Albendazole treatment of children with ascariasis enhances the vibriocidal antibody response to the live attenuated oral cholera vaccine CVD 103-HgR. J Infect Dis. 2000;182:1199–1206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

