Parapharyngeal abscess in children: five year retrospective study
- PMID: 20209282
- PMCID: PMC9446055
- DOI: 10.1016/s1808-8694(15)30544-9
Parapharyngeal abscess in children: five year retrospective study
Abstract
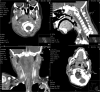
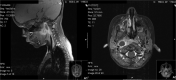
Lateropharyngeal and retropharyngeal abscesses are potentially life threatening infections in children
Aim: To review the etiologic, clinical, and imaging signs of lateropharyngeal and retropharyngeal abscesses in children as well as treatment-outcomes and complications using a surgical trans-oral approach.
Method: Retrospective analysis of 11 children, hospitalized in the last 5 years, with a diagnosis of lateropharyngeal (n = 8) and retropharyngeal (n = 3) abscesses, ages ranging from 0 to 12 years old. Charts and CT scans were reviewed.
Result: The average age of presentation was 3.3 years. Neck stiffness (64%) and odynophagia (55%) were the most common symptoms. Fever (64%), stiff neck (64%), bulging of the oropharyngeal wall (55%), mass in the neck (55%) and lymphadenopathy (36%) were the most prevalent physical findings. All these patients were submitted to surgical drainage using a trans-oral approach in the first 48 hours after admission. About 82% of the patients showed improvement after 48 hours, and 100% after 72 hours, without any complications.
Conclusion: Based on the good clinical outcomes and low incidence of complications, the present study suggests that antibiotic therapy complemented with a timely surgical treatment, is a valid treatment option in refractory parapharyngeal abscesses.
Figures
References
-
- Herzon FS, Martin AD. Medical and surgical treatment of peritonsillar, retropharyngeal, and parapharyngeal abscesses. Curr Infect Dis Resp. 2006;8:196–202. - PubMed
-
- Sethi DS, Stanley ES. Deep neck abscesses. J Laryngol Otol. 1994;108:138–143. - PubMed
-
- Broughton RA. Nonsurgical management of deep neck infections in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1992;11:14–18. - PubMed
-
- Barratt GE, Koopmann CF, Coulthard SW. Retropharyngeal abscess: A ten-year experience. Laryngoscope. 1984;94:455–463. - PubMed
-
- Thompson JW, Cohen SR, Reddix P. Retropharyngeal abscess in children: A retrospective and historial analysis. Laryngoscope. 1988;98:589–592. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

