Metastasis suppressor function of NM23-H1 requires its 3'-5' exonuclease activity
- PMID: 20209495
- PMCID: PMC2946830
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.25307
Metastasis suppressor function of NM23-H1 requires its 3'-5' exonuclease activity
Abstract
The metastasis suppressor NM23-H1 possesses 3 enzymatic activities in vitro, a nucleoside diphosphate kinase (NDPK), a protein histidine kinase and a more recently characterized 3'-5' exonuclease. Although the histidine kinase has been implicated in suppression of motility in breast carcinoma cell lines, potential relevance of the NDPK and 3'-5' exonuclease to metastasis suppressor function has not been addressed in detail. To this end, site-directed mutagenesis and biochemical analyses of bacterially expressed mutant NM23-H1 proteins have identified mutations that disrupt the 3'-5' exonuclease alone (Glu(5) to Ala, or E(5) A), the NDPK and histidine kinase activities tandemly (Y(52) A, H(118) F) or all 3 activities simultaneously (K(12) Q). Although forced expression of NM23-H1 potently suppressed spontaneous lung metastasis of subcutaneous tumor explants derived from the human melanoma cell line 1205LU, no significant metastasis suppressor activity was obtained with the exonuclease-deficient variants E(5) A and K(12) Q. The H(118) F mutant, which lacked both the NDPK and histidine kinase while retaining the 3'-5' exonuclease, also exhibited compromised suppressor activity. In contrast, each mutant retained the ability to suppress motility and invasive characteristics of 1205LU cells in culture, indicating that the NM23-H1 molecule possesses an additional activity(s) mediating these suppressor functions. These studies provide the first demonstration that the 3'-5' exonuclease activity of NM23-H1 is necessary for metastasis suppressor function and further indicate cooperativity of the 3 enzymatic activities of the molecule on suppression of the metastatic process.
Copyright © 2010 UICC.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

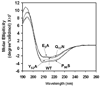
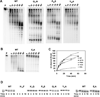

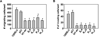

Similar articles
-
Potential roles of 3'-5' exonuclease activity of NM23-H1 in DNA repair and malignant progression.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2006 Aug;38(3-4):163-7. doi: 10.1007/s10863-006-9040-3. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2006. PMID: 17039395 Review.
-
Potential contributions of antimutator activity to the metastasis suppressor function of NM23-H1.Mol Cell Biochem. 2009 Sep;329(1-2):161-5. doi: 10.1007/s11010-009-0108-3. Epub 2009 Apr 21. Mol Cell Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19381784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Site-directed mutation of Nm23-H1. Mutations lacking motility suppressive capacity upon transfection are deficient in histidine-dependent protein phosphotransferase pathways in vitro.J Biol Chem. 1997 Feb 28;272(9):5525-32. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.9.5525. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9038158
-
The multiple regulation of metastasis suppressor NM23-H1 in cancer.Life Sci. 2021 Mar 1;268:118995. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118995. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33421524 Review.
-
The metastasis suppressor NM23-H1 possesses 3'-5' exonuclease activity.J Biol Chem. 2004 Apr 23;279(17):18073-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M400185200. Epub 2004 Feb 11. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14960567
Cited by
-
The Subcellular Localization and Oligomerization Preferences of NME1/NME2 upon Radiation-Induced DNA Damage.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 29;21(7):2363. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072363. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32235358 Free PMC article.
-
A critical evaluation of biochemical activities reported for the nucleoside diphosphate kinase/Nm23/Awd family proteins: opportunities and missteps in understanding their biological functions.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2011 Oct;384(4-5):331-9. doi: 10.1007/s00210-011-0651-9. Epub 2011 May 25. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21611737 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Protein-protein interactions: a mechanism regulating the anti-metastatic properties of Nm23-H1.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2011 Oct;384(4-5):351-62. doi: 10.1007/s00210-011-0646-6. Epub 2011 Jun 29. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21713383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small molecule activator of Nm23/NDPK as an inhibitor of metastasis.Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 19;8(1):10909. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29101-6. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30026594 Free PMC article.
-
The Function of NM23-H1/NME1 and Its Homologs in Major Processes Linked to Metastasis.Pathol Oncol Res. 2020 Jan;26(1):49-61. doi: 10.1007/s12253-020-00797-0. Epub 2020 Jan 28. Pathol Oncol Res. 2020. PMID: 31993913 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Steeg PS, Ouatas T, Halverson D, Palmieri D, Salerno M. Metastasis suppressor genes: basic biology and potential clinical use. Clin Breast Cancer. 2003;4:51–62. - PubMed
-
- Steeg PS, Bevilacqua G, Kopper L, Thorgerisson UR, Talmadge JE, Liotta LA, Sobel M. Evidence for a novel gene associated with low tumor metastatic potential. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1988;80:200–205. - PubMed
-
- Hartsough MT, Steeg PS. Nm23/nucleoside diphosphate kinase in human cancers. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2000;32:301–308. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal RP, Robinson B, Parks RE. Nucleoside diphosphokinase from erythrocytes. Methods Enzymol. 1978;51:376–386. - PubMed
-
- Sastre-Garau X, Lacombe ML, Jouve M, Veron M, Magdelenat H. Nucleoside diphosphate kinase/NM23 expression in breast cancer: lack of correlation with lymph-node metastasis. Int J Cancer. 1992;50:533–538. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

