Mutagenic repair of DNA interstrand crosslinks
- PMID: 20209624
- PMCID: PMC2892553
- DOI: 10.1002/em.20558
Mutagenic repair of DNA interstrand crosslinks
Abstract
Formation of DNA interstrand crosslinks (ICLs) in chromosomal DNA imposes acute obstruction of all essential DNA functions. For over 70 years bifunctional alkylators, also known as DNA crosslinkers, have been an important class of cancer chemotherapeutic regimens. The mechanisms of ICL repair remains largely elusive. Here, we review a eukaryotic mutagenic ICL repair pathway discovered by work from several laboratories. This repair pathway, alternatively termed recombination-independent ICL repair, involves the incision activities of the nucleotide excision repair (NER) mechanism and lesion bypass polymerase(s). Repair of the ICL is initiated by dual incisions flanking the ICL on one strand of the double helix; the resulting gap is filled in by lesion bypass polymerases. The remaining lesion is subsequently removed by a second round of NER reaction. The mutagenic repair of ICL likely interacts with other cellular mechanisms such as the Fanconi anemia pathway and recombinational repair of ICLs. These aspects will also be discussed.
Environ. Mol. Mutagen., 2010. (c) 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
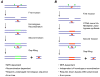
 ” indicates crosslinking moiety. Green arrows indicate positions of NER incision. DNA patches in green depicting error-free repair synthesis. DNA patches in red depicting error-prone repair synthesis.
” indicates crosslinking moiety. Green arrows indicate positions of NER incision. DNA patches in green depicting error-free repair synthesis. DNA patches in red depicting error-prone repair synthesis.References
-
- Berardini M, Mackay W, Loechler EL. Evidence for a recombination-independent pathway for the repair of DNA interstrand cross-links based on a site-specific study with nitrogen mustard. Biochemistry. 1997;36(12):3506–13. - PubMed
-
- Bienko M, Green CM, Crosetto N, Rudolf F, Zapart G, Coull B, Kannouche P, Wider G, Peter M, Lehmann AR, et al. Ubiquitin-binding domains in Y-family polymerases regulate translesion synthesis. Science. 2005;310(5755):1821–4. - PubMed
-
- Cassier-Chauvat C, Moustacchi E. Allelism between pso1-1 and rev3-1 mutants and between pso2-1 and snm1 mutants in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Genet. 1988;13(1):37–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

