Intravascular near-infrared fluorescence molecular imaging of atherosclerosis: toward coronary arterial visualization of biologically high-risk plaques
- PMID: 20210433
- PMCID: PMC3188610
- DOI: 10.1117/1.3280282
Intravascular near-infrared fluorescence molecular imaging of atherosclerosis: toward coronary arterial visualization of biologically high-risk plaques
Abstract
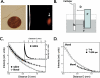
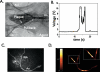
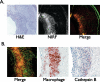
New imaging methods are urgently needed to identify high-risk atherosclerotic lesions prior to the onset of myocardial infarction, stroke, and ischemic limbs. Molecular imaging offers a new approach to visualize key biological features that characterize high-risk plaques associated with cardiovascular events. While substantial progress has been realized in clinical molecular imaging of plaques in larger arterial vessels (carotid, aorta, iliac), there remains a compelling, unmet need to develop molecular imaging strategies targeted to high-risk plaques in human coronary arteries. We present recent developments in intravascular near-IR fluorescence catheter-based strategies for in vivo detection of plaque inflammation in coronary-sized arteries. In particular, the biological, light transmission, imaging agent, and engineering principles that underlie a new intravascular near-IR fluorescence sensing method are discussed. Intravascular near-IR fluorescence catheters appear highly translatable to the cardiac catheterization laboratory, and thus may offer a new in vivo method to detect high-risk coronary plaques and to assess novel atherosclerosis biologics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Two-dimensional intravascular near-infrared fluorescence molecular imaging of inflammation in atherosclerosis and stent-induced vascular injury.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011 Jun 21;57(25):2516-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.02.036. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 21679853 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo near infrared fluorescence (NIRF) intravascular molecular imaging of inflammatory plaque, a multimodal approach to imaging of atherosclerosis.J Vis Exp. 2011 Aug 4;(54):2257. doi: 10.3791/2257. J Vis Exp. 2011. PMID: 21847078 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging of Atherosclerosis: Clinical and Intracoronary Evaluation of Indocyanine Green.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016 Sep;9(9):1087-1095. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2016.01.034. Epub 2016 Aug 17. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016. PMID: 27544892 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Near-infrared spectroscopy for intracoronary detection of lipid-rich plaques to understand atherosclerotic plaque biology in man and guide clinical therapy.J Intern Med. 2015 Aug;278(2):110-25. doi: 10.1111/joim.12381. Epub 2015 Jun 19. J Intern Med. 2015. PMID: 26096457 Review.
-
Intravascular molecular imaging: translating pathophysiology of atherosclerosis into human disease conditions.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2022 Dec 19;24(1):e1-e16. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jeac163. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2022. PMID: 36002376 Review.
Cited by
-
Improving quantification of intravascular fluorescence imaging using structural information.Phys Med Biol. 2012 Oct 21;57(20):6395-406. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/57/20/6395. Epub 2012 Sep 21. Phys Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 22996051 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular intravascular imaging approaches for atherosclerosis.Curr Cardiovasc Imaging Rep. 2014 Oct 1;7(10):9293. doi: 10.1007/s12410-014-9293-x. Curr Cardiovasc Imaging Rep. 2014. PMID: 25221639 Free PMC article.
-
Fiber-optic system for dual-modality imaging of glucose probes 18F-FDG and 6-NBDG in atherosclerotic plaques.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 18;9(9):e108108. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108108. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25233472 Free PMC article.
-
Two-dimensional intravascular near-infrared fluorescence molecular imaging of inflammation in atherosclerosis and stent-induced vascular injury.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011 Jun 21;57(25):2516-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.02.036. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 21679853 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal iron oxide nanoparticles for hybrid biomedical imaging.NMR Biomed. 2013 Jul;26(7):756-65. doi: 10.1002/nbm.2872. Epub 2012 Oct 15. NMR Biomed. 2013. PMID: 23065771 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Naghavi M., Libby P., Falk E., Casscells S. W., Litovsky S., Rumberger J., Badimon J. J., Stefanadis C., Moreno P., Pasterkamp G., Fayad Z., Stone P. H., Waxman S., Raggi P., Madjid M., Zarrabi A., Burke A., Yuan C., Fitzgerald P. J., Siscovick D. S., de Korte C. L., Aikawa M., Juhani Airaksinen K. E., Assmann G., Becker C. R., Chesebro J. H., Farb A., Galis Z. S., Jackson C., Jang I. K., Koenig W., Lodder R. A., March K., Demirovic J., Navab M., Priori S. G., Rekhter M. D., Bahr R., Grundy S. M., Mehran R., Colombo A., Boerwinkle E., Ballantyne C., W.Insull, Jr., Schwartz R. S., Vogel R., Serruys P. W., Hansson G. K., Faxon D. P., Kaul S., Drexler H., Greenland P., Muller J. E., Virmani R., Ridker P. M., Zipes D. P., Shah P. K., and Willerson J. T., “From vulnerable plaque to vulnerable patient: a call for new definitions and risk assessment strategies: part I,” Circulation CIRCAZ 108, 1664–1672 (2003).10.1161/01.CIR.0000087480.94275.97 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pogue B. W., Poplack S. P., McBride T. O., Wells W. A., Osterman K. S., Osterberg U. L., and Paulsen K. D., “Quantitative hemoglobin tomography with diffuse near-infrared spectroscopy: pilot results in the breast,” Radiology RADLAX 218, 261–266 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

