Efficient mucosal delivery of optical contrast agents using imidazole-modified chitosan
- PMID: 20210443
- PMCID: PMC2839797
- DOI: 10.1117/1.3309739
Efficient mucosal delivery of optical contrast agents using imidazole-modified chitosan
Abstract
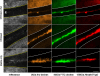
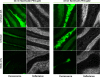
The clinical applicability of antibodies and plasmonic nanosensors as topically applied, molecule-specific optical diagnostic agents for noninvasive early detection of cancer and precancer is severely limited by our inability to efficiently deliver macromolecules and nanoparticles through mucosal tissues. We have developed an imidazole-functionalized conjugate of the polysaccharide chitosan (chitosan-IAA) to enhance topical delivery of contrast agents, ranging from small molecules and antibodies to gold nanoparticles up to 44 nm in average diameter. Contrast agent uptake and localization in freshly resected mucosal tissues was monitored using confocal microscopy. Chitosan-IAA was found to reversibly enhance mucosal permeability in a rapid, reproducible manner, facilitating transepithelial delivery of optical contrast agents. Permeation enhancement occurred through an active process, resulting in the delivery of contrast agents via a paracellular or a combined paracellular/transcellular route depending on size. Coadministration of epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted antibodies with chitosan-IAA facilitated specific labeling and discrimination between paired normal and malignant human oral biopsies. Together, these data suggest that chitosan-IAA is a promising topical permeation enhancer for mucosal delivery of optical contrast agents.
Figures
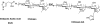
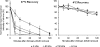


Similar articles
-
Delivery of optical contrast agents using Triton-X100, part 2: enhanced mucosal permeation for the detection of cancer biomarkers.J Biomed Opt. 2009 Mar-Apr;14(2):021013. doi: 10.1117/1.3090437. J Biomed Opt. 2009. PMID: 19405726 Free PMC article.
-
Buccal delivery of metformin: TR146 cell culture model evaluating the use of bioadhesive chitosan discs for drug permeability enhancement.Int J Pharm. 2013 Dec 31;458(2):254-61. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2013.10.026. Epub 2013 Oct 20. Int J Pharm. 2013. PMID: 24148665
-
Gadolinium-chitosan nanoparticles as a novel contrast agent for potential use in clinical bowel-targeted MRI: a feasibility study in healthy rats.Acta Radiol. 2012 Oct 1;53(8):900-7. doi: 10.1258/ar.2012.110017. Epub 2012 Aug 22. Acta Radiol. 2012. PMID: 22919051
-
Chitosan-based delivery systems for mucosal vaccines.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2012 Sep;9(9):1051-67. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2012.697455. Epub 2012 Jun 19. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2012. PMID: 22708875 Review.
-
Chitosan-based nanoparticles for mucosal delivery of RNAi therapeutics.Adv Genet. 2014;88:325-52. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800148-6.00011-0. Adv Genet. 2014. PMID: 25409611 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted nanogel conjugate for improved stability and cellular permeability of curcumin: synthesis, pharmacokinetics, and tumor growth inhibition.Mol Pharm. 2014 Sep 2;11(9):3112-22. doi: 10.1021/mp500290f. Epub 2014 Aug 5. Mol Pharm. 2014. PMID: 25072100 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation, characterization, and cellular associations of silicon logic-embedded vectors.Methods Enzymol. 2012;508:1-16. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-391860-4.00001-X. Methods Enzymol. 2012. PMID: 22449918 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in molecular imaging: targeted optical contrast agents for cancer diagnostics.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2012 Mar;7(3):429-45. doi: 10.2217/nnm.12.12. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2012. PMID: 22385200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of activated nucleoside analogs for the treatment of drug-resistant tumors by oral delivery of nanogel-drug conjugates.J Control Release. 2013 Apr 28;167(2):200-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.01.020. Epub 2013 Feb 4. J Control Release. 2013. PMID: 23385032 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering nanoparticles to overcome barriers to immunotherapy.Bioeng Transl Med. 2016 Jun 20;1(1):47-62. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10005. eCollection 2016 Mar. Bioeng Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 29313006 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nitin N., Carlson A. L., Muldoon T., El-Naggar A. K., Gillenwater A., and Richards-Kortum R., “Molecular imaging of glucose uptake in oral neoplasia following topical application of fluorescently labeled deoxy-glucose,” Int. J. Cancer IJCNAW 124(11), 2634–2642 (2008).10.1002/ijc.24222 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

