Enhanced antiproliferative and apoptotic response to combined treatment of gamma-tocotrienol with erlotinib or gefitinib in mammary tumor cells
- PMID: 20211018
- PMCID: PMC2841143
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-84
Enhanced antiproliferative and apoptotic response to combined treatment of gamma-tocotrienol with erlotinib or gefitinib in mammary tumor cells
Abstract
Background: Aberrant ErbB receptor signaling is associated with various types of malignancies. gamma-Tocotrienol is a member of the vitamin E family of compounds that displays potent anticancer activity that is associated with suppression in ErbB receptor phosphorylation and mitogenic signaling. Erlotinib and gefitinib are tyrosine kinase inhibitors that block ErbB1 receptor activation, whereas trastuzumab is a monoclonal antibody that has been designed to specifically inhibit ErbB2 receptor activation. However, the clinical effectiveness of these agents have been disappointing because of cooperation between different ErbB family members that can rescue cancer cells from agents directed against a single ErbB receptor subtype. It was hypothesized that targeting multiple ErbB receptor subtypes with combined treatment of gamma-tocotrienol and ErbB receptor inhibitors would provide greater anticancer effects than monotherapy targeting only a single ErbB receptor subtype.
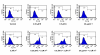
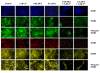
Methods: Highly malignant mouse +SA mammary epithelial cells were maintained in culture on serum-free defined media containing 10 ng/ml EGF as a mitogen. Cell viability wase determined by MTT assay, whereas Western blot and immunofluorescent staining was used to determine treatment effects on ErbB receptor subtype level and activation. Treatment-induced apoptosis was determined using annexin V staining and Western blot analysis of cleaved caspase-3 and PARP levels.
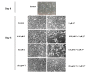
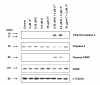
Results: Treatment with 3.5 microM gamma-tocotrienol, 0.5 microM erlotinib or 1.0 microM gefitinib alone, significantly inhibited +SA tumor cell growth. Combined treatment with subeffective doses of erlotinib (0.25 microM) or gefitinib (0.5 microM) with subeffective doses of gamma-tocotrienol (0.5-3.0 microM) significantly inhibited the growth and induced apoptosis in a dose-responsive manner. Trastuzumab treatment alone or in combination had no effect on +SA cell growth and viability. Combined treatment of gamma-tocotrienol with erlotinib or gefitinib also cause a large decrease in ErbB3, ErbB4, and to a lesser extent ErbB2 receptor levels, and EGF-dependent ErbB2-4 tyrosine phosphorylation (activation), but had no effect on ErbB1 receptor levels or activation.
Conclusion: Combination treatment of gamma-tocotrienol with specific ErbB receptor inhibitors is more effective in reducing mammary tumor cell growth and viability than high dose monotherapy, suggesting that targeting multiple ErbB receptors with combination therapy may significantly improve the therapeutic response in breast cancer patients.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

