Circulating surfactant protein -D is low and correlates negatively with systemic inflammation in early, untreated rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 20211020
- PMCID: PMC2888186
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2948
Circulating surfactant protein -D is low and correlates negatively with systemic inflammation in early, untreated rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Introduction: Surfactant protein D (SP-D) is a collectin with immuno-regulatory functions, which may depend on oligomerization. Anti-microbial and anti-inflammatory properties have been attributed to multimeric SP-D variants, while trimeric subunits per se have been suggested to enhance inflammation. Previously, we reported low circulating SP-D in early rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and the present investigation aims to extend these data by serial SP-D serum measurements, studies on synovial fluid, SP-D size distribution and genotyping in patients with early RA.
Methods: One-hundred-and-sixty disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) naïve RA patients with disease duration less than six months were studied prospectively for four years (CIMESTRA (Ciclosporine, Methotrexate, Steroid in RA) trial) including disease activity measures (C-reactive protein, joint counts and Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) score), autoantibodies, x-ray findings and SP-D. SP-D was quantified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and molecular size distribution was assessed by gel filtration chromatography. Further, SP-D Met11Thr single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) analysis was performed.
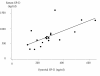
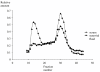
Results: Serum SP-D was significantly lower in RA patients at baseline compared with healthy controls (P < 0.001). SP-D increased slightly during follow-up (P < 0.001), but was still subnormal at four years after adjustment for confounders (P < 0.001). SP-D in synovial fluid was up to 2.5-fold lower than in serum. While multimeric variants were detected in serum, SP-D in synovial fluid comprised trimeric subunits only. There were no significant associations between genotype distribution and SP-D. Baseline SP-D was inversely associated to CRP and HAQ score. A similar relationship was observed regarding temporal changes in SP-D and CRP (zero to four years). SP-D was not associated to x-ray findings.
Conclusions: This study confirms that circulating SP-D is persistently subnormal in early and untreated RA despite a favourable therapeutic response obtained during four years of follow-up. SP-D correlated negatively to disease activity measures, but was not correlated with x-ray progression or SP-D genotype. These observations suggest that SP-D is implicated in RA pathogenesis at the protein level. The exclusive presence of trimeric SP-D in affected joints may contribute to the maintenance of joint inflammation.
Trial registration: (j.nr NCT00209859).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Surfactant Protein D in Respiratory and Non-Respiratory Diseases.Front Med (Lausanne). 2018 Feb 8;5:18. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2018.00018. eCollection 2018. Front Med (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 29473039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating surfactant protein D is decreased in early rheumatoid arthritis: a 1-year prospective study.Scand J Immunol. 2008 Jan;67(1):71-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2007.02039.x. Scand J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18052966
-
Surfactant protein-D, a potential mediator of inflammation in axial spondyloarthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018 Oct 1;57(10):1861-1865. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key187. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018. PMID: 29982797
-
Circadian rhythm and the influence of physical activity on circulating surfactant protein D in early and long-standing rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatol Int. 2011 Dec;31(12):1617-23. doi: 10.1007/s00296-010-1538-7. Epub 2010 May 29. Rheumatol Int. 2011. PMID: 20512337
-
Uncoupling of collagen II metabolism in newly diagnosed, untreated rheumatoid arthritis is linked to inflammation and antibodies against cyclic citrullinated peptides.J Rheumatol. 2010 Jun;37(6):1113-20. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.091265. Epub 2010 May 1. J Rheumatol. 2010. PMID: 20436079 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Factors influencing the measurement of plasma/serum surfactant protein D levels by ELISA.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 3;9(11):e111466. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111466. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25365324 Free PMC article.
-
An Insight into the Diverse Roles of Surfactant Proteins, SP-A and SP-D in Innate and Adaptive Immunity.Front Immunol. 2012 Jun 7;3:131. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00131. eCollection 2012. Front Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22701116 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variant associations of human SP-A and SP-D with acute and chronic lung injury.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012 Jan 1;17(2):407-29. doi: 10.2741/3935. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012. PMID: 22201752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of surfactant proteins A, B, C, and D in articular cartilage, synovial membrane and synovial fluid of healthy as well as patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.PLoS One. 2018 Sep 20;13(9):e0203502. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203502. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30235245 Free PMC article.
-
Surfactant Protein D in Respiratory and Non-Respiratory Diseases.Front Med (Lausanne). 2018 Feb 8;5:18. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2018.00018. eCollection 2018. Front Med (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 29473039 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Garred P, Madsen HO, Marquart H, Hansen TM, Sørensen SF, Petersen J, Volck B, Svejgaard A, Graudal NA, Rudd PM, Dwek RA, Sim RB, Andersen V. Two edged role of mannose binding lectin in rheumatoid arthritis: a cross sectional study. J Rheumatol. 2000;27:26–34. - PubMed
-
- Saevarsdottir S, Vikingsdottir T, Vikingsson A, Manfredsdottir V, Geirsson AJ, Valdimarsson H. Low Mannose Binding Lectin Predicts Poor Prognosis in Patients with Early Rheumatoid Arthritis. A Prospective Study. J Rheumatol. 2001;28:728–734. - PubMed
-
- Jacobsen S, Madsen HO, Klarlund M, Jensen T, Skjodt H, Jensen KE, Svejgaard A, Garred P. TIRA Group. The influence of mannose binding lectin polymorpisms on disease outcome in early polyarthritis. J Rheumatol. 2001;28:935–942. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

