Striking the target in Wnt-y conditions: intervening in Wnt signaling during cancer progression
- PMID: 20211149
- PMCID: PMC2897923
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2010.03.002
Striking the target in Wnt-y conditions: intervening in Wnt signaling during cancer progression
Abstract
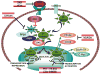
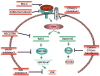
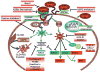
Wnt signaling can be divided into three pathways, namely the canonical Wnt/beta-catenin pathway, and the non-canonical (or heretical) Wnt/Ca(2+) and planar cell polarity (PCP) pathways. Although the canonical Wnt/beta-catenin pathway is the best described in cancer, increasing data points to the importance of the heretical Wnt pathways in several aspects of tumor progression. The recent advances in understanding the players and mechanisms by which these Wnt pathways contribute to cancer progression have led to the identification of numerous molecules that are already, or could be considered, targets for cancer therapy.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The involvement of noncanonical Wnt signaling in cancers.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Jan;133:110946. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110946. Epub 2020 Nov 16. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33212376 Review.
-
Recent Development of Wnt Signaling Pathway Inhibitors for Cancer Therapeutics.Curr Oncol Rep. 2019 Feb 4;21(2):12. doi: 10.1007/s11912-019-0763-9. Curr Oncol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30715618 Review.
-
Importance of Wnt signaling in the tumor stroma microenvironment.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2008 Sep;8(6):454-65. doi: 10.2174/156800908785699324. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2008. PMID: 18781892 Review.
-
Inhibition of nuclear Wnt signalling: challenges of an elusive target for cancer therapy.Br J Pharmacol. 2017 Dec;174(24):4589-4599. doi: 10.1111/bph.13963. Epub 2017 Aug 24. Br J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28752891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wnt/Planar cell polarity signaling: a new paradigm for cancer therapy.Mol Cancer Ther. 2009 Aug;8(8):2103-9. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-0282. Epub 2009 Aug 11. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009. PMID: 19671746 Review.
Cited by
-
Frizzled7 as an emerging target for cancer therapy.Cell Signal. 2012 Apr;24(4):846-51. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.12.009. Epub 2011 Dec 13. Cell Signal. 2012. PMID: 22182510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wnt signaling in the pathogenesis of human HIV-associated pain syndromes.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013 Sep;8(4):956-64. doi: 10.1007/s11481-013-9474-4. Epub 2013 Jun 5. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23737037 Free PMC article.
-
The functional roles of the circRNA/Wnt axis in cancer.Mol Cancer. 2022 May 5;21(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01582-0. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35513849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human placental trophoblast invasion and differentiation: a particular focus on Wnt signaling.Front Genet. 2013 Sep 26;4:190. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2013.00190. Front Genet. 2013. PMID: 24133501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression profile of frizzled receptors in human medulloblastomas.J Neurooncol. 2012 Jan;106(2):271-80. doi: 10.1007/s11060-011-0682-6. Epub 2011 Aug 18. J Neurooncol. 2012. PMID: 21850537
References
-
- Nusse R, Varmus HE. Wnt genes. Cell. 1992;69(7):1073–87. - PubMed
-
- Li Y, Bu G. LRP5/6 in Wnt signaling and tumorigenesis. Future Oncol. 2005;1(5):673–81. - PubMed
-
- Slusarski DC, V, Corces G, Moon RT. Interaction of Wnt and a Frizzled homologue triggers G-protein-linked phosphatidylinositol signalling. Nature. 1997;390(6658):410–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

