Assembly algorithms for next-generation sequencing data
- PMID: 20211242
- PMCID: PMC2874646
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2010.03.001
Assembly algorithms for next-generation sequencing data
Abstract
The emergence of next-generation sequencing platforms led to resurgence of research in whole-genome shotgun assembly algorithms and software. DNA sequencing data from the Roche 454, Illumina/Solexa, and ABI SOLiD platforms typically present shorter read lengths, higher coverage, and different error profiles compared with Sanger sequencing data. Since 2005, several assembly software packages have been created or revised specifically for de novo assembly of next-generation sequencing data. This review summarizes and compares the published descriptions of packages named SSAKE, SHARCGS, VCAKE, Newbler, Celera Assembler, Euler, Velvet, ABySS, AllPaths, and SOAPdenovo. More generally, it compares the two standard methods known as the de Bruijn graph approach and the overlap/layout/consensus approach to assembly.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: None.
Figures
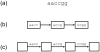

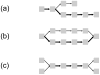

References
-
- Sanger F, Coulson AR, Barrell BG, Smith AJ, Roe BA. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980;143:161–78. - PubMed
-
- Mardis ER. The impact of next-generation sequencing technology on genetics. Trends Genet. 2008;24:133–41. - PubMed
-
- Morozova O, Marra MA. Applications of next-generation sequencing technologies in functional genomics. Genomics. 2008;92:255–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

