Receiver domain structure and function in response regulator proteins
- PMID: 20211578
- PMCID: PMC2847656
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mib.2010.01.015
Receiver domain structure and function in response regulator proteins
Abstract
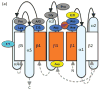
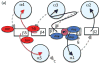
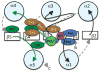
During signal transduction by two-component regulatory systems, sensor kinases detect and encode input information while response regulators (RRs) control output. Most receiver domains function as phosphorylation-mediated switches within RRs, but some transfer phosphoryl groups in multistep phosphorelays. Conserved features of receiver domain amino acid sequence correlate with structure and hence function. Receiver domains catalyze their own phosphorylation and dephosphorylation in reactions requiring a divalent cation. Molecular dynamics simulations are supplementing structural investigation of the conformational changes that underlie receiver domain switch function. As understanding of features shared by all receiver domains matures, factors conferring differences (e.g. in reaction rate or specificity) are receiving increased attention. Numerous examples of atypical receiver or pseudo-receiver domains that function without phosphorylation have recently been characterized.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Phyletic Distribution and Lineage-Specific Domain Architectures of Archaeal Two-Component Signal Transduction Systems.J Bacteriol. 2018 Mar 12;200(7):e00681-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00681-17. Print 2018 Apr 1. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 29263101 Free PMC article.
-
Proposed Role for KaiC-Like ATPases as Major Signal Transduction Hubs in Archaea.mBio. 2017 Dec 5;8(6):e01959-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01959-17. mBio. 2017. PMID: 29208747 Free PMC article.
-
The many faces of the helix-turn-helix domain: transcription regulation and beyond.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2005 Apr;29(2):231-62. doi: 10.1016/j.femsre.2004.12.008. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2005. PMID: 15808743 Review.
-
Diversity of structure and function of response regulator output domains.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2010 Apr;13(2):150-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2010.01.005. Epub 2010 Mar 11. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20226724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of restrained molecular dynamics to predict the conformations of phosphorylated receiver domains in two-component signaling systems.Proteins. 2017 Jan;85(1):155-176. doi: 10.1002/prot.25207. Epub 2016 Nov 20. Proteins. 2017. PMID: 27802580 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Lactoferricin B inhibits the phosphorylation of the two-component system response regulators BasR and CreB.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 Apr;11(4):M111.014720. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M111.014720. Epub 2011 Dec 2. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22138548 Free PMC article.
-
Two-component signaling pathways modulate drug resistance of Staphylococcus aureus (Review).Biomed Rep. 2020 Aug;13(2):5. doi: 10.3892/br.2020.1312. Epub 2020 Jun 9. Biomed Rep. 2020. PMID: 32607234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Two-Component Signal Transduction.J Mol Biol. 2016 Sep 25;428(19):3752-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2016.08.003. Epub 2016 Aug 9. J Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27519796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The atypical response regulator protein ChxR has structural characteristics and dimer interface interactions that are unique within the OmpR/PhoB subfamily.J Biol Chem. 2011 Sep 16;286(37):32606-16. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.220574. Epub 2011 Jul 20. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21775428 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the response regulator PhoP from Mycobacterium tuberculosis reveals a dimer through the receiver domain.Biochemistry. 2011 Jul 5;50(26):5948-57. doi: 10.1021/bi2005575. Epub 2011 Jun 13. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21634789 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Volz K. Structural conservation in the CheY superfamily. Biochemistry. 1993;32:11741–11753. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

