Many chromosomal genes modulate MarA-mediated multidrug resistance in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 20211899
- PMCID: PMC2863627
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01420-09
Many chromosomal genes modulate MarA-mediated multidrug resistance in Escherichia coli
Abstract
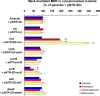
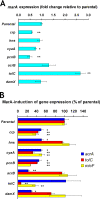
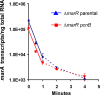
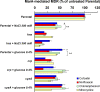
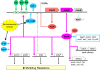
Multidrug resistance (MDR) in clinical isolates of Escherichia coli can be associated with overexpression of marA, a transcription factor that upregulates multidrug efflux and downregulates membrane permeability. Using random transposome mutagenesis, we found that many chromosomal genes and environmental stimuli affected MarA-mediated antibiotic resistance. Seven genes affected resistance mediated by MarA in an antibiotic-specific way; these were mostly genes encoding unrelated enzymes, transporters, and unknown proteins. Other genes affected MarA-mediated resistance to all antibiotics tested. These genes were acrA, acrB, and tolC (which encode the major MarA-regulated multidrug efflux pump AcrAB-TolC), crp, cyaA, hns, and pcnB (four genes involved in global regulation of gene expression), and the unknown gene damX. The last five genes affected MarA-mediated MDR by altering marA expression or MarA function specifically on acrA. These findings demonstrate that MarA-mediated MDR is regulated at multiple levels by different genes and stimuli, which makes it both complex and fine-tuned and interconnects it with global cell regulation and metabolism. Such a regulation could contribute to the adaptation and spread of MDR strains and may be targeted to treat antibiotic-resistant E. coli and related pathogens.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role for tandem duplication and lon protease in AcrAB-TolC- dependent multiple antibiotic resistance (Mar) in an Escherichia coli mutant without mutations in marRAB or acrRAB.J Bacteriol. 2006 Jun;188(12):4413-23. doi: 10.1128/JB.01502-05. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16740948 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of geraniol resistance of Escherichia coli by MarA overexpression.J Biosci Bioeng. 2013 Mar;115(3):253-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2012.10.009. Epub 2012 Nov 16. J Biosci Bioeng. 2013. PMID: 23168261
-
AcrB-AcrA Fusion Proteins That Act as Multidrug Efflux Transporters.J Bacteriol. 2015 Nov 2;198(2):332-42. doi: 10.1128/JB.00587-15. Print 2016 Jan 15. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 26527645 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of organic solvent tolerance level of Escherichia coli by overexpression of stress-responsive genes.Extremophiles. 1998 Aug;2(3):239-48. doi: 10.1007/s007920050066. Extremophiles. 1998. PMID: 9783171 Review.
-
AcrAB and related multidrug efflux pumps of Escherichia coli.J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2001 Apr;3(2):215-8. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2001. PMID: 11321576 Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement of MarR and YedS in carbapenem resistance in a clinical isolate of Escherichia coli from China.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Apr;57(4):1935-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02445-12. Epub 2013 Jan 14. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23318808 Free PMC article.
-
Benzoate- and Salicylate-Tolerant Strains of Escherichia coli K-12 Lose Antibiotic Resistance during Laboratory Evolution.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016 Dec 30;83(2):e02736-16. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02736-16. Print 2017 Jan 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27793830 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing the Efficacy of Chloramphenicol Therapy for Escherichia coli by Targeting the Secondary Resistome.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Jan 12;13(1):73. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13010073. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38247632 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis of denuded glycan recognition by SPOR domains in bacterial cell division.Nat Commun. 2019 Dec 5;10(1):5567. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13354-4. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31804467 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-Genome Sequencing and Genetic Analysis Reveal Novel Stress Responses to Individual Constituents of Essential Oils in Escherichia coli.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Mar 19;84(7):e02538-17. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02538-17. Print 2018 Apr 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29374037 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alekshun, M. N., and S. B. Levy. 2007. Molecular mechanisms of antibacterial multidrug resistance. Cell 128:1037-1050. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

