Six-Minute Walk Test demonstrates motor fatigue in spinal muscular atrophy
- PMID: 20211907
- PMCID: PMC2839195
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181d3e308
Six-Minute Walk Test demonstrates motor fatigue in spinal muscular atrophy
Abstract
Background: In spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), weakness, decreased endurance, and fatigue limit mobility. Scales have been developed to measure function across the wide spectrum of disease severity. However, these scales typically are observer dependent, and scores are based on sums across Likert-scaled items. The Six-Minute Walk Test (6MWT) is an objective, easily administered, and standardized evaluation of functional exercise capacity that has been proven reliable in other neurologic disorders and in children.
Methods: To study the performance of the 6MWT in SMA, 18 ambulatory participants were evaluated in a cross-sectional study. Clinical measures were 6MWT, 10-m walk/run, Hammersmith Functional Motor Scale-Expanded (HFMSE), forced vital capacity, and handheld dynamometry. Associations between the 6MWT total distance and other outcomes were analyzed using Spearman correlation coefficients. A paired t test was used to compare the mean distance walked in the first and sixth minutes.
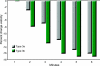
Results: The 6MWT was associated with the HFMSE score (r = 0.83, p < 0.0001), 10-m walk/run (r = -0.87, p < 0.0001), and knee flexor strength (r = 0.62, p = 0.01). Gait velocity decreased during successive minutes in nearly all participants. The average first minute distance (57.5 m) was significantly more than the sixth minute distance (48 m) (p = 0.0003).
Conclusion: The Six-Minute Walk Test (6MWT) can be safely performed in ambulatory patients with spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), correlates with established outcome measures, and is sensitive to fatigue-related changes. The 6MWT is a promising candidate outcome measure for clinical trials in ambulatory subjects with SMA.
Figures
Comment in
-
Six-minute walk test demonstrates motor fatigue in spinal muscular atrophy.Neurology. 2010 Sep 21;75(12):1121-2; author reply 1122. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181f00304. Neurology. 2010. PMID: 20855858 No abstract available.
References
-
- Emery AE. Population frequencies of inherited neuromuscular diseases: a world survey. Neuromuscul Disord 1991;1:19–29. - PubMed
-
- Piepers S, van den Berg LH, Brugman F, et al. A natural history study of late onset spinal muscular atrophy types 3b and 4. J Neurol 2008;255:1400–1404. - PubMed
-
- de Groot IJ, de Witte LP. Physical complaints in ageing persons with spinal muscular atrophy. J Rehabil Med 2005;37:258–262. - PubMed
-
- Iannaccone ST, White M, Browne R, Russman B, Buncher R, Samaha FJ. Muscle fatigue in spinal muscular atrophy. J Child Neurol 1997;12:321–326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- DK63608/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1U54 NS0657-12-01/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- DK-04-021/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AR52274/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- 5P01HD32062/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- NS49639/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01NS37949/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- N01-AR-50-227450/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- NS50573/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HL80107/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- NS42372/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01CA069398/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS48125/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RR24160/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K12NS01698/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS46487/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RC2HD064525/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 5K12NS01698/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HD44430/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- DK52431/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- NS50095/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HD057036/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 1 UL1 RR024156-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 2P01NS040828-6A11/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024160/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- NS48843/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS45686/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AR0526446-03/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- DE16280/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- NS58259/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS52619/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS043264-04 A1/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL098163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
