Attenuated baroreflex control of sympathetic nerve activity in obese Zucker rats by central mechanisms
- PMID: 20211978
- PMCID: PMC2876806
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.186387
Attenuated baroreflex control of sympathetic nerve activity in obese Zucker rats by central mechanisms
Abstract
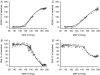
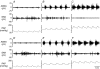
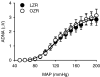
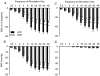
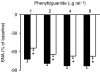
Adult obese Zucker rats (OZRs) have reduced sympathetic responses to evoked changes in arterial pressure (AP) compared to lean Zucker rats (LZRs). This study examined whether attenuated sympathetic baroreflexes in OZRs may be due to altered sensory or central mechanisms. The OZRs had elevated baseline splanchnic sympathetic nerve activity (SNA) and mean AP (MAP) compared to age-matched LZRs under urethane anaesthesia (P < 0.05). Aortic depressor nerve activity (ADNA) was measured while AP was altered by infusions of phenylephrine or nitroprusside (+/-60 mmHg over 60-90 s) in rats treated with atropine and propranolol to eliminate changes in heart rate. Although baseline ADNA was higher in the hypertensive OZRs, the relationship between MAP and ADNA was comparable in OZRs and LZRs. In contrast, electrical stimulation of the ADN afferent fibres (5 s train, 2 ms pulses, 4 V, 0.5-48 Hz) produced dramatically smaller reductions in SNA and MAP in OZRs compared to LZRs (P < 0.05). After blockade of alpha-adrenergic receptors to prevent sympathetically mediated depressor responses, OZRs still had reduced sympathetic responses to stimulation of the ADN. In addition, stimulation of vagal afferent nerves electrically or with phenylbiguanide (1, 2, 4 and 8 microg, i.v.) produced smaller inhibitions of SNA in OZRs compared with LZRs (P < 0.05). These data suggest that attenuated sympathetic baroreflexes are the result of altered central mechanisms in OZRs, and not deficits in the responsiveness of aortic baroreceptors to AP. Furthermore, central deficits in the regulation of SNA in OZRs extend to other sympathoinhibitory reflexes initiated by vagal afferent nerves.
Figures
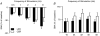
Comment in
-
Does our fat tell our brain what to do? A sympathetic' appraisal.J Physiol. 2010 May 1;588(Pt 9):1389-90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2010.190124. J Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20436042 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Impairment of sympathetic baroreceptor reflexes in obese Zucker rats.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007 Oct;293(4):H2543-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01201.2006. Epub 2007 Aug 17. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17704284
-
Baroreflex and somato-reflex control of blood pressure, heart rate and renal sympathetic nerve activity in the obese Zucker rat.Exp Physiol. 2011 Jul;96(7):623-34. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2011.057638. Epub 2011 Apr 28. Exp Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21527543
-
Preserved glycemic control and baroreflex efficacy in young adult hypertensive female obese Zucker rats.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2021 Jul 1;321(1):R62-R78. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00341.2020. Epub 2021 May 12. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33978481 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac baroreflexes and hypertension.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1994 Oct;21(10):791-802. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1994.tb02448.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1994. PMID: 7867230 Review.
-
How sympathetic tone maintains or alters arterial pressure.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 1995;9(4):343-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.1995.tb00508.x. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 1995. PMID: 8566933 Review.
Cited by
-
Impaired blood pressure compensation following hemorrhage in conscious obese Zucker rats.Life Sci. 2013 Aug 14;93(5-6):214-219. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2013.06.006. Epub 2013 Jun 16. Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23782999 Free PMC article.
-
Diet-induced obesity severely impairs myelinated aortic baroreceptor reflex responses.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012 May 15;302(10):H2083-91. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01200.2011. Epub 2012 Mar 9. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22408022 Free PMC article.
-
Improved glucose homeostasis in male obese Zucker rats coincides with enhanced baroreflexes and activation of the nucleus tractus solitarius.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2018 Dec 1;315(6):R1195-R1209. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00195.2018. Epub 2018 Sep 26. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30256679 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of sex and sedentary conditions on sympathetic burst characteristics in prepubertal, postpubertal, and young adult rats.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2024 May 1;136(5):1170-1181. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00649.2023. Epub 2024 Mar 21. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2024. PMID: 38511214 Free PMC article.
-
Exaggerated sympathoexcitatory reflexes develop with changes in the rostral ventrolateral medulla in obese Zucker rats.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2016 Aug 1;311(2):R243-53. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00085.2016. Epub 2016 Jun 8. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27280427 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alemzadeh R, Tushaus KM. Modulation of adipoinsular axis in prediabetic Zucker diabetic fatty rats by diazoxide. Endocrinol. 2004;145:5476–5484. - PubMed
-
- Andresen MC. Short- and long-term determinants of baroreceptor function in aged normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats. Circ Res. 1984;54:750–759. - PubMed
-
- Angell-James Characteristics of single aortic and right subclavian baroreceptor fibre activity in rabbits with chronic renal hypertension. Circ Res. 1973;32:149–161. - PubMed
-
- Angell-James Arterial baroreceptor activity in rabbits with experimental atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 1974;34:27–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

