Spatiotemporal control of nanooptical excitations
- PMID: 20212153
- PMCID: PMC2851794
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0913556107
Spatiotemporal control of nanooptical excitations
Abstract
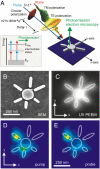
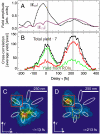
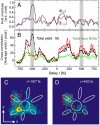
The most general investigation and exploitation of light-induced processes require simultaneous control over spatial and temporal properties of the electromagnetic field on a femtosecond time and nanometer length scale. Based on the combination of polarization pulse shaping and time-resolved two-photon photoemission electron microscopy, we demonstrate such control over nanoscale spatial and ultrafast temporal degrees of freedom of an electromagnetic excitation in the vicinity of a nanostructure. The time-resolved cross-correlation measurement of the local photoemission yield reveals the switching of the nanolocalized optical near-field distribution with a lateral resolution well below the diffraction limit and a temporal resolution on the femtosecond time scale. In addition, successful adaptive spatiotemporal control demonstrates the flexibility of the method. This flexible simultaneous control of temporal and spatial properties of nanophotonic excitations opens new possibilities to tailor and optimize the light-matter interaction in spectroscopic methods as well as in nanophotonic applications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Weiner AM. Femtosecond pulse shaping using spatial light modulators. Rev Sci Instrum. 2000;71:1929–1960.
-
- Brixner T, Gerber G. Femtosecond polarization pulse shaping. Opt Lett. 2001;26:557–559. - PubMed
-
- Brixner T, Krampert G, Niklaus P, Gerber G. Generation and characterization of polarization-shaped femtosecond laser pulses. Appl Phys B: Lasers Opt. 2002;74:s133–s144.
-
- Rice SA, Zhao M. Optical Control of Molecular Dynamics. New York: Wiley Interscience; 2000. pp. 39–240.
-
- Brumer PW, Shapiro M. Principles of the Quantum Control of Molecular Processes. New York: Wiley; 2003. pp. 117–321.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

