Maximum entropy models for antibody diversity
- PMID: 20212159
- PMCID: PMC2851784
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1001705107
Maximum entropy models for antibody diversity
Abstract
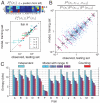
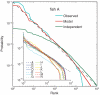
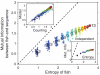
Recognition of pathogens relies on families of proteins showing great diversity. Here we construct maximum entropy models of the sequence repertoire, building on recent experiments that provide a nearly exhaustive sampling of the IgM sequences in zebrafish. These models are based solely on pairwise correlations between residue positions but correctly capture the higher order statistical properties of the repertoire. By exploiting the interpretation of these models as statistical physics problems, we make several predictions for the collective properties of the sequence ensemble: The distribution of sequences obeys Zipf's law, the repertoire decomposes into several clusters, and there is a massive restriction of diversity because of the correlations. These predictions are completely inconsistent with models in which amino acid substitutions are made independently at each site and are in good agreement with the data. Our results suggest that antibody diversity is not limited by the sequences encoded in the genome and may reflect rapid adaptation to antigenic challenges. This approach should be applicable to the study of the global properties of other protein families.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Pal C, Papp B, Lercher M. An integrated view of protein evolution. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7:337–348. - PubMed
-
- Branden C, Tooze J. Introduction to Protein Structure. New York: Garland Science; 1991.
-
- Cordes MH, Davidson AR, Sauer RT. Sequence space, folding and protein design. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1996;6:3–10. - PubMed
-
- Socolich M, et al. Evolutionary information for specifying a protein fold. Nature. 2005;437:512–518. - PubMed
-
- Russ WP, Lowery DM, Mishra P, Yaffe MB, Ranganathan R. Natural-like function in artificial ww domains. Nature. 2005;437:579–583. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

