HO* radicals induce an unexpected high proportion of tandem base lesions refractory to repair by DNA glycosylases
- PMID: 20212167
- PMCID: PMC2851781
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1000193107
HO* radicals induce an unexpected high proportion of tandem base lesions refractory to repair by DNA glycosylases
Abstract
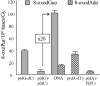
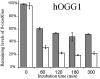
Reaction of HO(*) radicals with double-stranded calf thymus DNA produces high levels of 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-oxodGuo) and, to a minor extent, 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyadenosine (8-oxodAdo). Formation of the hydroxylated purine lesions is explained by addition of HO(*) to the C8 position of the purine moiety. It has been reported that tandem lesions containing a formylamine residue neighboring 8-oxodGuo could be produced through addition of a transiently generated pyrimidine peroxyl radical onto the C8 of an adjacent purine base. Formation of such tandem lesions accounted for approximately 10% of the total 8-oxodGuo. In the present work we show that addition of HO(*) onto the C8 of purine accounts for only approximately 5% of the generated 8-oxodGuo. About 50% of the 8-hydroxylated purine lesions, including 8-oxodGuo and 8-oxodAdo, are involved in tandem damage and are produced by peroxyl addition onto the C8 of a vicinal purine base. In addition, the remaining 45% of the 8-oxodGuo are produced by an electron transfer reaction, providing an explanation for the higher yield of formation of 8-oxodGuo compared to 8-oxodAdo. Interestingly, we show that >40% of the 8-oxodGuo involved in tandem lesions is refractory to excision by DNA glycosylases. Altogether our results demonstrate that, subsequently to a single oxidation event, peroxidation reactions significantly increase the yield of formation of hydroxylated purine modifications, generating a high proportion of tandem lesions partly refractory to base excision repair.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Lindahl T. Instability and decay of the primary structure of DNA. Nature. 1993;362:709–715. - PubMed
-
- Cadet J, Douki T, Gasparutto D, Ravanat J-L. Oxidative damage to DNA: Formation, measurement and biochemical features. Mutat Res. 2003;531:5–23. - PubMed
-
- Kasai H, Tanooka H, Nishimura S. Formation of 8-hydroxyguanine residues in DNA by X-irradiation. Gann. 1984;75:1037–1039. - PubMed
-
- Cadet J, et al. DNA damage and radical reactions: Mechanistic aspects, formation in cells and repair studies. Chimia (Aarau) 2008;62:742–749.
-
- Hall DB, Holmlin RE, Barton JK. Oxidative DNA damage through long-range electron transfer. Nature. 1996;382:731–735. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

