Adipocyte modulation of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- PMID: 20212278
- PMCID: PMC2925122
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.897330
Adipocyte modulation of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol
Abstract
Background: Adipose harbors a large depot of free cholesterol. However, a role for adipose in cholesterol lipidation of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) in vivo is not established. We present the first evidence that adipocytes support transfer of cholesterol to HDL in vivo as well as in vitro and implicate ATP-binding cassette subfamily A member 1 (ABCA1) and scavenger receptor class B type I (SR-BI), but not ATP-binding cassette subfamily G member 1 (ABCG1), cholesterol transporters in this process.
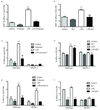
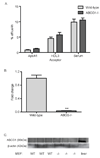
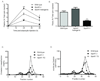
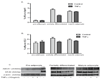
Methods and results: Cholesterol efflux from wild-type, ABCA1(-/-), SR-BI(-/-), and ABCG1(-/-) adipocytes to apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I) and HDL3 were measured in vitro. 3T3L1 adipocytes, labeled with (3)H-cholesterol, were injected intraperitoneally into wild-type, apoA-I transgenic, and apoA-I(-/-) mice, and tracer movement onto plasma HDL was monitored. Identical studies were performed with labeled wild-type, ABCA1(-/-), or SR-BI(-/-) mouse embryonic fibroblast adipocytes. The effect of tumor necrosis factor-alpha on transporter expression and cholesterol efflux was monitored during adipocyte differentiation. Cholesterol efflux to apoA-I and HDL3 was impaired in ABCA1(-/-) and SR-BI(-/-) adipocytes, respectively, with no effect observed in ABCG1(-/-) adipocytes. Intraperitoneal injection of labeled 3T3L1 adipocytes resulted in increased HDL-associated (3)H-cholesterol in apoA-I transgenic mice but reduced levels in apoA-I(-/-) animals. Intraperitoneal injection of labeled ABCA1(-/-) or SR-BI(-/-) adipocytes reduced plasma counts relative to their respective controls. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha reduced both ABCA1 and SR-BI expression and impaired cholesterol efflux from partially differentiated adipocytes.
Conclusions: These data suggest a novel metabolic function of adipocytes in promoting cholesterol transfer to HDL in vivo and implicate adipocyte SR-BI and ABCA1, but not ABCG1, in this process. Furthermore, adipocyte modulation of HDL may be impaired in adipose inflammatory disease states such as type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Apolipoprotein AI and high-density lipoprotein have anti-inflammatory effects on adipocytes via cholesterol transporters: ATP-binding cassette A-1, ATP-binding cassette G-1, and scavenger receptor B-1.Circ Res. 2013 May 10;112(10):1345-54. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.300581. Epub 2013 Mar 15. Circ Res. 2013. PMID: 23501697 Free PMC article.
-
SR-BI associates with ABCG1 and inhibits ABCG1-mediated cholesterol efflux from cells to high-density lipoprotein 3.Lipids Health Dis. 2012 Sep 17;11:118. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-11-118. Lipids Health Dis. 2012. PMID: 22984960 Free PMC article.
-
Nascent HDL formation in hepatocytes and role of ABCA1, ABCG1, and SR-BI.J Lipid Res. 2012 Mar;53(3):446-455. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M017079. Epub 2011 Dec 20. J Lipid Res. 2012. PMID: 22190590 Free PMC article.
-
Role of apoA-I, ABCA1, LCAT, and SR-BI in the biogenesis of HDL.J Mol Med (Berl). 2006 Apr;84(4):276-94. doi: 10.1007/s00109-005-0030-4. Epub 2006 Feb 25. J Mol Med (Berl). 2006. PMID: 16501936 Review.
-
Foam cells in atherosclerosis.Clin Chim Acta. 2013 Sep 23;424:245-52. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.06.006. Epub 2013 Jun 16. Clin Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 23782937 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel mechanisms of action of the biologicals in rheumatic diseases.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2014 Aug;47(1):6-16. doi: 10.1007/s12016-013-8359-x. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2014. PMID: 23345026 Review.
-
In vivo triglyceride synthesis in subcutaneous adipose tissue of humans correlates with plasma HDL parameters.Atherosclerosis. 2016 Aug;251:147-152. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.06.024. Epub 2016 Jun 13. Atherosclerosis. 2016. PMID: 27323227 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic unpredictable mild stress promotes atherosclerosis via adipose tissue dysfunction in ApoE-/- mice.PeerJ. 2023 Sep 4;11:e16029. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16029. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37692113 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Deletion of Adipocyte Abca1 (ATP-Binding Cassette Transporter A1) Impairs Diet-Induced Obesity.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018 Apr;38(4):733-743. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.309880. Epub 2018 Jan 18. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018. PMID: 29348118 Free PMC article.
-
Adipocyte phospholipid transfer protein and lipoprotein metabolism.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015 Feb;35(2):316-22. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.303764. Epub 2014 Dec 4. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015. PMID: 25477345 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ford ES, Giles WH, Dietz WH. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome among US adults: findings from the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Jama. 2002;287:356–359. - PubMed
-
- Gordon DJ, Rifkind BM. High-density lipoprotein--the clinical implications of recent studies. N Engl J Med. 1989;321:1311–1316. - PubMed
-
- Brunham LR, Singaraja RR, Duong M, Timmins JM, Fievet C, Bissada N, Kang MH, Samra A, Fruchart JC, McManus B, Staels B, Parks JS, Hayden MR. Tissue-specific roles of ABCA1 influence susceptibility to atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009;29:548–554. - PubMed
-
- Timmins JM, Lee JY, Boudyguina E, Kluckman KD, Brunham LR, Mulya A, Gebre AK, Coutinho JM, Colvin PL, Smith TL, Hayden MR, Maeda N, Parks JS. Targeted inactivation of hepatic Abca1 causes profound hypoalphalipoproteinemia and kidney hypercatabolism of apoA-I. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:1333–1342. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

