Liquid chromatography with post-column reagent addition of ammonia in methanol coupled to negative ion electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry for determination of phenoxyacid herbicides and their degradation products in surface water
- PMID: 20212919
- PMCID: PMC2832344
- DOI: 10.4137/aci.s3148
Liquid chromatography with post-column reagent addition of ammonia in methanol coupled to negative ion electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry for determination of phenoxyacid herbicides and their degradation products in surface water
Abstract
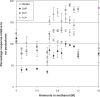
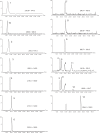
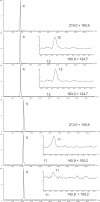
A new liquid chromatography (LC)-negative ion electrospray ionization (ESI(-))-tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) method with post-column addition of ammonia in methanol has been developed for the analysis of acid herbicides: 2,4-dichlorophenoxy acetic acid, 4-chloro-o-tolyloxyacetic acid, 2-(2-methyl-4-chlorophenoxy)butyric acid, mecoprop, dichlorprop, 4-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy) butyric acid, 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxy propionic acid, dicamba and bromoxynil, along with their degradation products: 4-chloro-2-methylphenol, 2,4-dichlorophenol, 2,4,5-trichlorophenol and 3,5-dibromo-4-hydroxybenzoic acid. The samples were extracted from the surface water matrix using solid-phase extraction (SPE) with a polymeric sorbent and analyzed with LC ESI(-) with selected reaction monitoring (SRM) using a three-point confirmation approach. Chromatography was performed on a Zorbax Eclipse XDB-C18 (50 x 4.6 mm i.d., 1.8 mum) with a gradient elution using water-methanol with 2 mM ammonium acetate mobile phase at a flow rate of 0.15 mL/min. Ammonia in methanol (0.8 M) was added post-column at a flow rate of 0.05 mL/min to enhance ionization of the degradation products in the MS source. One SRM transition was used for quantitative analysis while the second SRM along with the ratio of SRM1/SRM2 within the relative standard deviation determined by standards for each individual pesticide and retention time match were used for confirmation. The standard deviation of ratio of SRM1/SRM2 obtained from standards run on the day of analysis for different phenoxyacid herbicides ranged from 3.9 to 18.5%. Limits of detection (LOD) were between 1 and 15 ng L(-1) and method detection limits (MDL) with strict criteria requiring <25% deviation of peak area from best-fit line for both SRM1 and SRM2 ranged from 5 to 10 ng L(-1) for acid ingredients (except dicamba at 30 ng L(-1)) and from 2 to 30 ng L(-1) for degradation products. The SPE-LC-ESI(-) MS/MS method permitted low nanogram-per-liter determination of pesticides and degradation products for surface water samples.
Keywords: liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry; pesticides; phenoxyacid herbicides; post-column reagent addition; water analysis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Trace level determination of selected organophosphorus pesticides and their degradation products in environmental air samples by liquid chromatography-positive ion electrospray tandem mass spectrometry.J Environ Sci Health B. 2008 May;43(4):323-32. doi: 10.1080/03601230801941667. J Environ Sci Health B. 2008. PMID: 18437620
-
Determination of phenoxyacid herbicides and their phenolic metabolites in surface and drinking water.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2002;16(2):134-41. doi: 10.1002/rcm.557. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2002. PMID: 11754259
-
High-performance liquid chromatography with paired ion electrospray ionization (PIESI) tandem mass spectrometry for the highly sensitive determination of acidic pesticides in water.Anal Chim Acta. 2013 Aug 20;792:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2013.05.054. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Anal Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 23910961
-
Forced degradation and impurity profiling: recent trends in analytical perspectives.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013 Dec;86:11-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2013.07.013. Epub 2013 Jul 31. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013. PMID: 23969330 Review.
-
Determination of trichothecenes A (T-2 toxin, HT-2 toxin, and diacetoxyscirpenol) in the tissues of broilers using liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013 Dec 30;942-943:88-97. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2013.10.034. Epub 2013 Oct 25. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 24231141 Review.
References
-
- Health Canada Guidelines for Canadian drinking water quality summary table, prepared for Federal-Provincial-Territorial Committee on drinking water of the Federal-Provincial-Territorial Committee on Health and the Environment, May 2008.
-
- Summary of Canadian Water Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Aquatic Life, Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment, 2006.
-
- Dąbrowska D, Kot-Wasik A, Namieśnik J. Stability Studies of Selected Phenoxyacid herbicides in water samples and determination of their transformation products. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 2006;77:245–51. - PubMed
-
- Fukumori F, Hausinger RP. Purification and characterization of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetate/α-ketoglutarate dioxygenase. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:24311–7. - PubMed
-
- Waite DT, Cessna AJ, Grover R, Kerr LA, Snihura AD. Environmental concentrations of agricultural herbicides: 2,4-D and triallate. J Environ Qual. 2002;31:129–44. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

