Long-term interferon-α treatment suppresses tumor growth but promotes metastasis capacity in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 20213095
- PMCID: PMC11828181
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-010-0848-1
Long-term interferon-α treatment suppresses tumor growth but promotes metastasis capacity in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: To elucidate the effect of IFN-α treatment on tumor growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
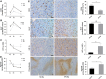
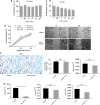
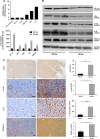
Methods: IFN-α administration was conducted in nude mice using an orthotopic implantation model of human HCC, and the key molecular markers in the IFN-α treatment was detected by immunohistochemistry staining and PCR array.
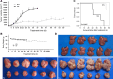
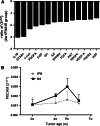
Results: Up to 12 weeks of IFN-α treatment significantly suppressed tumor growth of HCC, but relatively increased the number of circulating tumor cells, which might be due to the enhanced tumor hypoxia as well as up-regulation of metastasis-related genes, such as HIF-1α, c-met, u-PA, PDGF-A, and IL-8. However, IFN-α had no direct effect on migration and invasion of HCC cells.
Conclusions: IFN-α has janus face of consistently suppressing HCC growth, however, promoting tumor metastasis capacity, which is of clinical indication for the scientific administration of IFN-α and the similar antiangiogenesis drugs for their dual effect on tumor growth and metastasis.
Figures
References
-
- Bix G, Castello R, Burrows M et al (2006) Endorepellin in vivo: targeting the tumor vasculature and retarding cancer growth and metabolism. J Natl Cancer Inst 98:1634–1646 - PubMed
-
- Bristow RG, Hill RP (2008) Hypoxia and metabolism. Hypoxia, DNA repair and genetic instability. Nat Rev Cancer 8:180–192 - PubMed
-
- Chan DA, Giaccia AJ (2007) Hypoxia, gene expression, and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 26:333–339 - PubMed
-
- Chang YS, Adnane J, Trail PA et al (2007) Sorafenib (BAY 43–9006) inhibits tumor growth and vascularization and induces tumor apoptosis and hypoxia in RCC xenograft models. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 59:561–574 - PubMed
-
- Fenton BM, Paoni SF (2007) The addition of AG-013736 to fractionated radiation improves tumor response without functionally normalizing the tumor vasculature. Cancer Res 67:9921–9928 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

