The efficacy of combination therapy using adeno-associated virus-TRAIL targeting to telomerase activity and cisplatin in a mice model of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 20213096
- PMCID: PMC11827828
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-010-0841-8
The efficacy of combination therapy using adeno-associated virus-TRAIL targeting to telomerase activity and cisplatin in a mice model of hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) functions as a soluble cytokine and has been demonstrated significant antitumor activity against a variety of cancer cell lines without toxicity to most normal cells. Cisplatin is a potent anticancer agent and is widely used in the clinical for treatment of human cancers. Adeno-associated virus (AAV2) is a promising gene delivery vehicle for its advantage of low pathogenicity and long-term gene expression. However, lack of tissue specificity caused low efficiency of AAV transfer to target cells. The promoter of human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) is a good candidate to enhance targeting efficiency of AAV in cancer cells. Although AAV-mediated TRAIL controlled by hTERT promoter (AAV-hTERT-TRAIL) has obvious antitumor activity, the tumor cannot be completely eradicated. In this study, we first examined the effectiveness of combination therapy of cisplatin and AAV-hTERT-TRAIL on human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in vitro and in vivo.
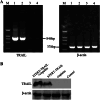
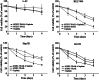
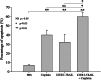
Methods: For in vitro experiments, tumor cell lines were treated with cisplatin, virus, or both. The transgene TRAIL expression controlled by hTERT promoter was evaluated in BEL7404 HCC cell line. Cytotoxicity was performed by MTT analysis. Cell apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry analysis. The in vivo antitumor efficacy of combination treatment with cisplatin and AAV-hTERT-TRAIL was assessed in human hepatocellular carcinoma xenografts mouse model.
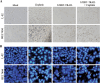
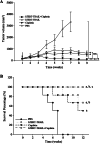
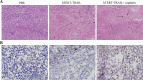
Results: The enhanced TRAIL expression was observed in BEL7404 cells treated with AAV-hTERT-TRAIL plus cisplatin. Treatment with both AAV-hTERT-TRAIL and cisplatin exhibited stronger cytotoxicity and induced more significant apoptosis in cancer cells compared with AAV-hTERT-TRAIL or cisplatin alone, respectively. Moreover, in animal experiments, the combined treatment greatly suppressed tumor growth and resulted in tumor cell death.
Conclusions: AAV-mediated therapeutic gene expression in combination with chemotherapy provides a promising therapeutic strategy for human cancers. These data suggest that combined use of AAV-hTERT-TRAIL and cisplatin may have potential clinical application.
Figures
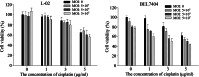
Similar articles
-
Synergistic suppression effect on tumor growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by combining oncolytic adenovirus carrying XAF1 with cisplatin.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015 Mar;141(3):419-29. doi: 10.1007/s00432-014-1835-8. Epub 2014 Sep 21. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25240826 Free PMC article.
-
Potent antitumor effect of TRAIL mediated by a novel adeno-associated viral vector targeting to telomerase activity for human hepatocellular carcinoma.J Gene Med. 2008 May;10(5):518-26. doi: 10.1002/jgm.1177. J Gene Med. 2008. PMID: 18338833
-
Synergistic antitumor effect of AAV-mediated TRAIL expression combined with cisplatin on head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2011 Feb 3;11:54. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-54. BMC Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21291526 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Aug 29;8(8):CD004064. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004064.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28850174 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Adenoviral gene therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma: a review.Hepatol Int. 2013 Mar;7(1):48-58. doi: 10.1007/s12072-012-9367-2. Epub 2012 Apr 25. Hepatol Int. 2013. PMID: 26201621
-
Development of optimized AAV3 serotype vectors: mechanism of high-efficiency transduction of human liver cancer cells.Gene Ther. 2012 Apr;19(4):375-84. doi: 10.1038/gt.2011.105. Epub 2011 Jul 21. Gene Ther. 2012. PMID: 21776025 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting adeno-associated virus and adenoviral gene therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Jan 7;22(1):326-37. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i1.326. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 26755879 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatocellular Carcinoma Is a Natural Target for Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) 2 Vectors.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 15;14(2):427. doi: 10.3390/cancers14020427. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35053588 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis-Inducing TNF Superfamily Ligands for Cancer Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 27;13(7):1543. doi: 10.3390/cancers13071543. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33801589 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arany I, Safirstein RL (2003) Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity. Semin Nephrol 23:460–464 - PubMed
-
- Ashkenazi A, Pai RC, Fong S, Leung S, Lawrence DA, Marsters SA, Blackie C, Chang L, Mcmurtrey AE, Hebert A, Deforge L, Koumenis IL, Lewis D, Harris L, Bussiere J, Koeppen H, Shahrokh Z, Schwall RH (1999) Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2 ligand. J Clin Invest 104:155–162 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Büning H, Perabo L, Coutelle O, Quadt-Humme S, Hallek M (2008) Recent developments in adeno-associated virus vector technology. J Gene Med 10:717–733 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

