Optimized combination therapy using bortezomib, TRAIL and TLR agonists in established breast tumors
- PMID: 20213120
- PMCID: PMC6993141
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-010-0834-0
Optimized combination therapy using bortezomib, TRAIL and TLR agonists in established breast tumors
Abstract
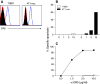
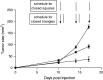
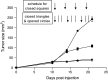
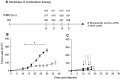
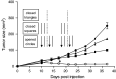
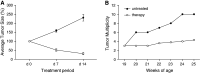
TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is a member of the TNF family of cytokines, which can induce apoptosis in various tumor cells by engaging the receptors, DR4 and DR5. Bortezomib (Velcade) is a proteasome inhibitor that has been approved for patients with multiple myeloma. There is some experimental evidence in preclinical models that bortezomib can enhance the susceptibility of tumors to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. In this study, we investigated the effects of TRAIL-induced death using an agonistic antibody to the TRAIL receptor DR5 (alpha-DR5) in combination with bortezomib administered to mice previously injected with breast cancer cells (TUBO). This combination had some beneficial therapeutic effect, which was significantly enhanced by the co-administration of a Toll-like receptor 9 agonist (CpG). In contrast, single agent treatments had little effect on tumor growth. In addition, we evaluated the effect of combination with alpha-DR5, bortezomib, and CpG in the prevention/treatment of spontaneous mammary tumors in Balb-neuT mice. In this model, which is more difficult to treat, we observed dramatic antitumor effects of alpha-DR5, bortezomib and CpG combination therapy. Since such a mouse model more accurately reflects the immunological tolerance that exists in human cancer, our results strongly suggest that these combination strategies could be directly applied to the therapy for cancer patients.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

