Effect of tumour-cell-derived or recombinant keratinocyte growth factor (KGF) on proliferation and radioresponse of human epithelial tumour cells (HNSCC) and normal keratinocytes in vitro
- PMID: 20213138
- PMCID: PMC2855434
- DOI: 10.1007/s00411-010-0271-7
Effect of tumour-cell-derived or recombinant keratinocyte growth factor (KGF) on proliferation and radioresponse of human epithelial tumour cells (HNSCC) and normal keratinocytes in vitro
Abstract
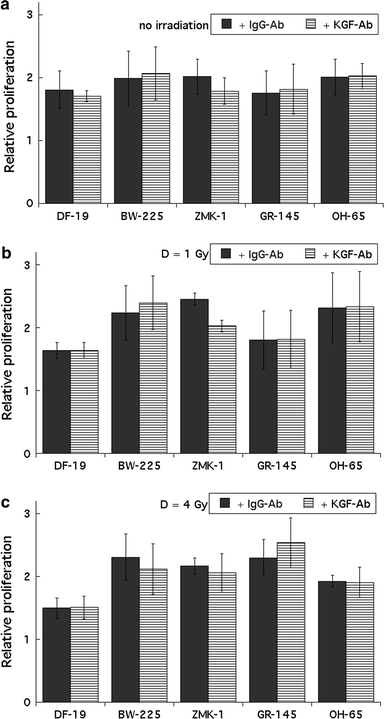
Purpose of this work was to test the effect of tumour-cell-derived keratinocyte growth factor (KGF) or recombinant KGF (palifermin) on cell proliferation and radiation response of human HNSCC cells and normal keratinocytes in vitro. Four tumour cell cultures derived from head and neck squamous cell carcinomas, primary keratinocytes, and immortalized keratinocytes were analysed. Fibroblasts, the natural source of KGF protein, served as controls. KGF expression was observed in primary and immortalized keratinocytes, fibroblasts, and in tumour cells, while significant KGF receptor expression was only found in keratinocytes. Recombinant KGF as well as tumour-cell-derived KGF caused a significant growth stimulation and radioprotection in keratinocytes, which was abolished by a neutralizing anti-KGF antibody. This indicates that tumour-cell-derived KGF is biologically active. In the tumour cell lines, no significant growth stimulation was induced by recombinant KGF, and the neutralizing antibody did not influence tumour cell growth or radiation response. Our results indicate that the normal, paracrine KGF regulatory mechanisms, which are based on KGF receptor expression, are lost in malignant cells, with the consequence of irresponsiveness of the tumour cells to exogenous KGF. In face of the amelioration of the radiation response of normal epithelia, demonstrated in various clinical and various preclinical animal studies, recombinant KGF represents a candidate for the selective protection of normal epithelia during radio(chemo) therapy of squamous cell carcinoma.
Figures
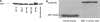
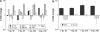

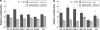
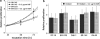
Similar articles
-
Effects of keratinocyte growth factor on the proliferation and radiation survival of human squamous cell carcinoma cell lines in vitro and in vivo.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1998 Jan 1;40(1):177-87. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(97)00561-0. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1998. PMID: 9422575
-
The mitogenic effect of KGF and the expression of its cell surface receptor on cultured normal and malignant human oral keratinocytes and on contiguous fibroblasts.J Oral Pathol Med. 1997 Aug;26(7):327-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.1997.tb00224.x. J Oral Pathol Med. 1997. PMID: 9250933
-
Human colon fibroblasts induce differentiation and proliferation of intestinal epithelial cells through the direct paracrine action of keratinocyte growth factor.J Cell Physiol. 2009 Jul;220(1):204-13. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21752. J Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19326389
-
Keratinocyte growth factor expression and activity in cancer: implications for use in patients with solid tumors.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006 Jun 21;98(12):812-24. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djj228. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006. PMID: 16788155 Review.
-
An overview on keratinocyte growth factor: from the molecular properties to clinical applications.Protein Pept Lett. 2014 Mar;21(3):306-17. doi: 10.2174/09298665113206660115. Protein Pept Lett. 2014. PMID: 24188496 Review.
Cited by
-
AhR‑E2F1‑KGFR signaling is involved in KGF‑induced intestinal epithelial cell proliferation.Mol Med Rep. 2017 May;15(5):3019-3026. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6368. Epub 2017 Mar 23. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28339052 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial expression of keratinocytes growth factor in oral precancer lesions.Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2016 May-Jun;13(3):199-205. doi: 10.4103/1735-3327.182148. Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2016. PMID: 27274338 Free PMC article.
-
Radioprotective Effects of Dermatan Sulfate in a Preclinical Model of Oral Mucositis-Targeting Inflammation, Hypoxia and Junction Proteins without Stimulating Proliferation.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jun 6;19(6):1684. doi: 10.3390/ijms19061684. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29882770 Free PMC article.
-
Lamotrigine decreases MRP8 and IL-7 in rat models of intractable epilepsy secondary to focal cortical dysplasia.Exp Ther Med. 2016 Dec;12(6):3694-3698. doi: 10.3892/etm.2016.3806. Epub 2016 Oct 14. Exp Ther Med. 2016. PMID: 28105099 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast growth factor 7 signalling is disrupted in colorectal cancer and is a potential marker of field cancerisation.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2019 Jun;10(3):429-436. doi: 10.21037/jgo.2019.02.11. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31183192 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

