Hippocampal interneuron loss in an APP/PS1 double mutant mouse and in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 20213270
- PMCID: PMC3038332
- DOI: 10.1007/s00429-010-0242-4
Hippocampal interneuron loss in an APP/PS1 double mutant mouse and in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
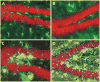
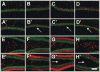
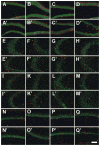
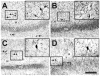
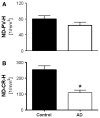
Hippocampal atrophy and neuron loss are commonly found in Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, the underlying molecular mechanisms and the fate in the AD hippocampus of subpopulations of interneurons that express the calcium-binding proteins parvalbumin (PV) and calretinin (CR) has not yet been properly assessed. Using quantitative stereologic methods, we analyzed the regional pattern of age-related loss of PV- and CR-immunoreactive (ir) neurons in the hippocampus of mice that carry M233T/L235P knocked-in mutations in presenilin-1 (PS1) and overexpress a mutated human beta-amyloid precursor protein (APP), namely, the APP(SL)/PS1 KI mice, as well as in APP(SL) mice and PS1 KI mice. We found a loss of PV-ir neurons (40-50%) in the CA1-2, and a loss of CR-ir neurons (37-52%) in the dentate gyrus and hilus of APP(SL)/PS1 KI mice. Interestingly, comparable PV- and CR-ir neuron losses were observed in the dentate gyrus of postmortem brain specimens obtained from patients with AD. The loss of these interneurons in AD may have substantial functional repercussions on local inhibitory processes in the hippocampus.
Figures
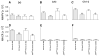

Similar articles
-
Loss of Hippocampal Calretinin and Parvalbumin Interneurons in the 5XFAD Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.ASN Neuro. 2020 Jan-Dec;12:1759091420925356. doi: 10.1177/1759091420925356. ASN Neuro. 2020. PMID: 32423230 Free PMC article.
-
Subfield and layer-specific depletion in calbindin-D28K, calretinin and parvalbumin immunoreactivity in the dentate gyrus of amyloid precursor protein/presenilin 1 transgenic mice.Neuroscience. 2008 Jul 31;155(1):182-91. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.05.023. Epub 2008 May 24. Neuroscience. 2008. PMID: 18583063 Free PMC article.
-
Age-related changes of neuron numbers in the frontal cortex of a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Brain Struct Funct. 2011 Sep;216(3):227-37. doi: 10.1007/s00429-011-0305-1. Epub 2011 Mar 16. Brain Struct Funct. 2011. PMID: 21409417 Free PMC article.
-
Calretinin interneurons are early targets of extracellular amyloid-beta pathology in PS1/AbetaPP Alzheimer mice hippocampus.J Alzheimers Dis. 2010;21(1):119-32. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2010-100066. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010. PMID: 20413859
-
Presenilin transgenic mice as models of Alzheimer's disease.Brain Struct Funct. 2010 Mar;214(2-3):127-43. doi: 10.1007/s00429-009-0227-3. Epub 2009 Nov 18. Brain Struct Funct. 2010. PMID: 19921519 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prefrontal parvalbumin interneurons deficits mediate early emotional dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2023 Jan;48(2):391-401. doi: 10.1038/s41386-022-01435-w. Epub 2022 Oct 13. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 36229597 Free PMC article.
-
Circuit Mechanisms of Neurodegenerative Diseases: A New Frontier With Miniature Fluorescence Microscopy.Front Neurosci. 2019 Oct 31;13:1174. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.01174. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31736701 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Parvalbumin-Positive Neuron Loss and Amyloid-β Deposits in the Frontal Cortex of Alzheimer's Disease-Related Mice.J Alzheimers Dis. 2019;72(4):1323-1339. doi: 10.3233/JAD-181190. J Alzheimers Dis. 2019. PMID: 31743995 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenic Mouse Models of Alzheimer's Disease: An Integrative Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 12;23(10):5404. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105404. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alterations of sleep oscillations in Alzheimer's disease: A potential role for GABAergic neurons in the cortex, hippocampus, and thalamus.Brain Res Bull. 2022 Sep;187:181-198. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2022.07.002. Epub 2022 Jul 15. Brain Res Bull. 2022. PMID: 35850189 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arai H, Emson PC, Mountjoy CQ, Carassco LH, Heizmann CW. Loss of parvalbumin-immunoreactive neurones from cortex in Alzheimer-type dementia. Brain Res. 1987;418:164–169. - PubMed
-
- Bano D, Nicotera P. Ca2+ signals and neuronal death in brain ischemia. Stroke. 2007;38(2 Suppl):674–676. - PubMed
-
- Barrow PA, Empson RM, Gladwell SJ, Anderson CM, Killick R, Yu X, Jefferys JG, Duff K. Functional phenotype in transgenic mice expressing mutant human presenilin-1. Neurobiol Dis. 2000;7(2):119–126. - PubMed
-
- Bazzett TJ, Becker JB, Falik RC, Albin RL. Chronic intrastriatal quinolinic acid produces reversible changes in perikaryal calbindin and parvalbumin immunoreactivity. Neuroscience. 1994;60(4):837–841. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

