Relaxin family peptide systems and the central nervous system
- PMID: 20213277
- PMCID: PMC11115692
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-010-0304-z
Relaxin family peptide systems and the central nervous system
Abstract
Since its discovery in the 1920s, relaxin has enjoyed a reputation as a peptide hormone of pregnancy. However, relaxin and other relaxin family peptides are now associated with numerous non-reproductive physiologies and disease states. The new millennium bought with it the sequence of the human genome and subsequently new directions for relaxin research. In 2002, the ancestral relaxin gene RLN3 was identified from genome databases. The relaxin-3 peptide is highly expressed in a small region of the brain and in species from teleost to primates and has both conserved sequence and sites of expression. Combined with the discovery of the relaxin family peptide receptors, interest in the role of the relaxin family peptides in the central nervous system has been reignited. This review explores the relaxin family peptides that are expressed in or act upon the brain, the receptors that mediate their actions, and what is currently known of their functions.
Figures
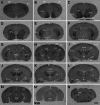
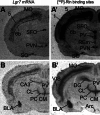
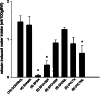
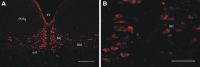
Similar articles
-
Relaxin-family peptide and receptor systems in brain: insights from recent anatomical and functional studies.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;612:119-37. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-74672-2_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 18161485 Review.
-
RLN3/RXFP3 Signaling in the PVN Inhibits Magnocellular Neurons via M-like Current Activation and Contributes to Binge Eating Behavior.J Neurosci. 2020 Jul 8;40(28):5362-5375. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2895-19.2020. Epub 2020 Jun 12. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32532885 Free PMC article.
-
Sex- and age-specific differences in relaxin family peptide receptor expression within the hippocampus and amygdala in rats.Neuroscience. 2015 Jan 22;284:337-348. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.10.006. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 25313002
-
[Relaxin-3 and relaxin family peptide receptors--from structure to functions of a newly discovered mammalian brain system].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2014;68:851-64. doi: 10.5604/17322693.1110163. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2014. PMID: 24988606 Review. Polish.
-
Estrous Cycle Modulation of Feeding and Relaxin-3/Rxfp3 mRNA Expression: Implications for Estradiol Action.Neuroendocrinology. 2021;111(12):1201-1218. doi: 10.1159/000513830. Epub 2020 Dec 17. Neuroendocrinology. 2021. PMID: 33333517
Cited by
-
International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. XCV. Recent advances in the understanding of the pharmacology and biological roles of relaxin family peptide receptors 1-4, the receptors for relaxin family peptides.Pharmacol Rev. 2015;67(2):389-440. doi: 10.1124/pr.114.009472. Pharmacol Rev. 2015. PMID: 25761609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Indole-Containing Amidinohydrazones as Nonpeptide, Dual RXFP3/4 Agonists: Synthesis, Structure-Activity Relationship, and Molecular Modeling Studies.J Med Chem. 2021 Dec 23;64(24):17866-17886. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c01081. Epub 2021 Dec 2. J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34855388 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism for insulin-like peptide 5 distinguishing the homologous relaxin family peptide receptor 3 and 4.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 11;6:29648. doi: 10.1038/srep29648. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27404393 Free PMC article.
-
The Relaxin-3 Receptor, RXFP3, Is a Modulator of Aging-Related Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 15;23(8):4387. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084387. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35457203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the relaxin-3/RXFP3 system: a patent review for the last two decades.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2024 Jan-Feb;34(1-2):71-81. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2024.2338099. Epub 2024 Apr 4. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2024. PMID: 38573177 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hisaw F. Experimental relaxation of the pubic ligament of the guinea pig. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1926;23:661–663.
-
- Fevold HL, Hisaw FL, Meyer RK. The relaxative hormone of the corpus luteum: its purification and concentration. J Am Chem Soc. 1930;52:3340–3348. doi: 10.1021/ja01371a051. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

