Concurrent inhibition of NF-kappaB, cyclooxygenase-2, and epidermal growth factor receptor leads to greater anti-tumor activity in pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 20213764
- PMCID: PMC3093967
- DOI: 10.1002/jcb.22523
Concurrent inhibition of NF-kappaB, cyclooxygenase-2, and epidermal growth factor receptor leads to greater anti-tumor activity in pancreatic cancer
Retraction in
-
Retraction: "Concurrent inhibition of NF-κB, cyclooxygenase-2, and epidermal growth factor receptor leads to greater anti-tumor activity in pancreatic cancer" by Ali et al.J Cell Biochem. 2016 Aug;117(8):1961. doi: 10.1002/jcb.25586. J Cell Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27301888 Free PMC article.
Abstract
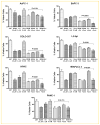
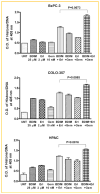
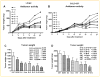
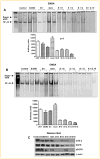
Inactivation of survival pathways such as NF-kappaB, cyclooxygenase (COX-2), or epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling individually may not be sufficient for the treatment of advanced pancreatic cancer (PC) as suggested by recent clinical trials. 3,3'-Diindolylmethane (B-DIM) is an inhibitor of NF-kappaB and COX-2 and is a well-known chemopreventive agent. We hypothesized that the inhibition of NF-kappaB and COX-2 by B-DIM concurrently with the inhibition of EGFR by erlotinib will potentiate the anti-tumor effects of cytotoxic drug gemcitabine, which has been tested both in vitro and in vivo. Inhibition of viable cells in seven PC cell lines treated with B-DIM, erlotinib, or gemcitabine alone or their combinations was evaluated using 3-(4,5-dimetylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. Significant inhibition in cell viability was observed in PC cells expressing high levels of COX-2, EGFR, and NF-kappaB proteins. The observed inhibition was associated with an increase in apoptosis as assessed by ELISA. A significant down-regulation in the expression of COX-2, NF-kappaB, and EGFR in BxPC-3, COLO-357, and HPAC cells was observed, suggesting that simultaneous targeting of EGFR, NF-kappaB, and COX-2 is more effective than targeting either signaling pathway separately. Our in vitro results were further supported by in vivo studies showing that B-DIM in combination with erlotinib and gemcitabine was significantly more effective than individual agents. Based on our preclinical in vitro and in vivo results, we conclude that this multi-targeted combination could be developed for the treatment of PC patients whose tumors express high levels of COX-2, EGFR, and NF-kappaB.
(c) 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Apoptosis-inducing effect of erlotinib is potentiated by 3,3'-diindolylmethane in vitro and in vivo using an orthotopic model of pancreatic cancer.Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Jun;7(6):1708-19. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0354. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008. Retraction in: Mol Cancer Ther. 2018 Oct;17(10):2266. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-18-0522. PMID: 18566242 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Simultaneous targeting of the epidermal growth factor receptor and cyclooxygenase-2 pathways for pancreatic cancer therapy.Mol Cancer Ther. 2005 Dec;4(12):1943-51. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-05-0065. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005. PMID: 16373709
-
Potentiation of the effect of erlotinib by genistein in pancreatic cancer: the role of Akt and nuclear factor-kappaB.Cancer Res. 2006 Nov 1;66(21):10553-9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-2333. Cancer Res. 2006. Retraction in: Cancer Res. 2018 Sep 15;78(18):5472. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-1168. PMID: 17079479 Retracted.
-
NF-κB in the crosshairs: Rethinking an old riddle.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2018 Feb;95:108-112. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2017.12.020. Epub 2017 Dec 23. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29277662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemoprevention strategies for pancreatic cancer.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010 Jun;7(6):347-56. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2010.61. Epub 2010 May 4. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010. PMID: 20440279 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Retraction: "Concurrent inhibition of NF-κB, cyclooxygenase-2, and epidermal growth factor receptor leads to greater anti-tumor activity in pancreatic cancer" by Ali et al.J Cell Biochem. 2016 Aug;117(8):1961. doi: 10.1002/jcb.25586. J Cell Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27301888 Free PMC article.
-
Aspirin use and pancreatic cancer risk: A systematic review of observational studies.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Dec;98(51):e18033. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018033. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31860953 Free PMC article.
-
Difluorinated-curcumin (CDF): a novel curcumin analog is a potent inhibitor of colon cancer stem-like cells.Pharm Res. 2011 Apr;28(4):827-38. doi: 10.1007/s11095-010-0336-y. Epub 2010 Dec 14. Pharm Res. 2011. PMID: 21161336 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin chemosensitizes 5-fluorouracil resistant MMR-deficient human colon cancer cells in high density cultures.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 3;9(1):e85397. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085397. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24404205 Free PMC article.
-
RETRACTED: Increased Ras GTPase activity is regulated by miRNAs that can be attenuated by CDF treatment in pancreatic cancer cells.Cancer Lett. 2012 Jun 28;319(2):173-181. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.01.013. Epub 2012 Jan 17. Cancer Lett. 2012. Retraction in: Cancer Lett. 2018 Feb 1;414:313. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.11.030. PMID: 22261338 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Ali S, El-Rayes BF, Sarkar FH, Philip PA. Simultaneous targeting of the epidermal growth factor receptor and cyclooxygenase-2 pathways for pancreatic cancer therapy. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005;4:1943–1951. - PubMed
-
- Bergmann F, Breinig M, Hopfner M, Rieker RJ, Fischer L, Kohler C, Esposito I, Kleeff J, Herpel E, Ehemann V, Friess H, Schirmacher P, Kern MA. Expression pattern and functional relevance of epidermal growth factor receptor and cyclooxygenase-2: Novel chemotherapeutic targets in pancreatic endocrine tumors? Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104:171–181. - PubMed
-
- Cai Y, Lee YF, Li G, Liu S, Bao BY, Huang J, Hsu CL, Chang C. A new prostate cancer therapeutic approach: Combination of androgen ablation with COX-2 inhibitor. Int J Cancer. 2008;123:195–201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

