Adipocytokines, insulin resistance, and coronary atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 20213808
- PMCID: PMC2910412
- DOI: 10.1002/art.27376
Adipocytokines, insulin resistance, and coronary atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objective: The prevalence of subclinical coronary atherosclerosis is increased in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and the increased risk is associated with insulin resistance. Adipocytokines have been linked to obesity, insulin resistance, inflammation, and coronary heart disease in the general population. This study was undertaken to examine the hypothesis that adipocytokines affect insulin resistance and coronary atherosclerosis among patients with RA.
Methods: The coronary calcium score, homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) index, and serum adipocytokine (leptin, adiponectin, resistin, and visfatin) concentrations were determined in 169 patients with RA. The independent effect of each adipocytokine on insulin resistance according to the HOMA-IR index and on coronary artery calcification determined by electron beam computed tomography was assessed in models adjusted for age, race, sex, body mass index (BMI), traditional cardiovascular risk factors, and inflammation mediators. In addition, an interaction analysis was performed to evaluate whether the effect of the HOMA-IR index on the coronary calcium score is moderated by adipocytokines.
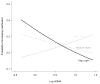
Results: Increased concentrations of leptin were associated with a higher HOMA-IR index, even after adjustment for age, race, sex, BMI, traditional cardiovascular risk factors, and inflammation mediators (P < 0.001), but concentrations of visfatin (P = 0.06), adiponectin (P = 0.55), and resistin (P = 0.98) showed no association with the HOMA-IR index. None of the adipocytokines was independently associated with the coronary calcium score (all P > 0.05). Serum leptin concentrations showed a significant interaction with the HOMA-IR index (P for multivariate interaction = 0.02). Increasing leptin concentrations attenuated the increased risk of coronary calcification related to insulin resistance. Serum concentrations of the other adipocytokines showed no significant interactions with the HOMA-IR index (each P > 0.05).
Conclusion: Leptin is associated with insulin resistance in patients with RA but, paradoxically, attenuates the effects of insulin resistance on coronary calcification.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Adipocytokines in systemic lupus erythematosus: relationship to inflammation, insulin resistance and coronary atherosclerosis.Lupus. 2009 Aug;18(9):799-806. doi: 10.1177/0961203309103582. Lupus. 2009. PMID: 19578104 Free PMC article.
-
Adipocytokines in primary antiphospholipid syndrome: potential markers of low-grade inflammation, insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2012 Nov-Dec;30(6):871-8. Epub 2012 Dec 17. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2012. PMID: 22935544
-
Adipocytokines are associated with radiographic joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2009 Jul;60(7):1906-14. doi: 10.1002/art.24626. Arthritis Rheum. 2009. PMID: 19565493 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating levels of adiponectin, leptin, resistin and visfatin in non-diabetics patients with hidradenitis suppurativa.Arch Dermatol Res. 2020 Oct;312(8):595-600. doi: 10.1007/s00403-019-02018-4. Epub 2019 Nov 30. Arch Dermatol Res. 2020. PMID: 31786710
-
Adipokines, insulin resistance, and coronary artery calcification.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008 Jul 15;52(3):231-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.04.016. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008. PMID: 18617073 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Utility of a novel inflammatory marker, GlycA, for assessment of rheumatoid arthritis disease activity and coronary atherosclerosis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2015 May 9;17(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0646-x. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 25956924 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise is Associated With Increased Small HDL Particle Concentration and Decreased Vascular Stiffness in Rheumatoid Arthritis.J Clin Rheumatol. 2018 Dec;24(8):417-421. doi: 10.1097/RHU.0000000000000809. J Clin Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29846271 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation and hypertension in rheumatoid arthritis.J Rheumatol. 2013 Nov;40(11):1806-11. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.130394. Epub 2013 Sep 1. J Rheumatol. 2013. PMID: 23996293 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin resistance and levels of adipokines in patients with untreated early rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Rheumatol. 2016 Jan;35(1):43-53. doi: 10.1007/s10067-015-3106-8. Epub 2015 Nov 3. Clin Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26526677 Free PMC article.
-
Independent associations of total and high molecular weight adiponectin with cardiometabolic risk and surrogate markers of enhanced early atherogenesis in black and white patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a cross-sectional study.Arthritis Res Ther. 2013 Sep 20;15(5):R128. doi: 10.1186/ar4308. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013. PMID: 24286214 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chung CP, Oeser A, Raggi P, Gebretsadik T, Shintani AK, Sokka T, et al. Increased coronary-artery atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis: relationship to disease duration and cardiovascular risk factors. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(10):3045–53. - PubMed
-
- Tilg H, Moschen AR. Adipocytokines: mediators linking adipose tissue, inflammation and immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6(10):772–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL-67964/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007569/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM-07569/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- TL1 RR024978/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 RR024977/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL065082/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HL-65082/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AR056116/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P60-AR-056116/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL067964/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

