A pilot study on the effects of a team building process on the perception of work environment in an integrative hospital for neurological rehabilitation
- PMID: 20214789
- PMCID: PMC2841088
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6882-10-10
A pilot study on the effects of a team building process on the perception of work environment in an integrative hospital for neurological rehabilitation
Abstract
Background: Neurological rehabilitation is one of the most care-intensive challenges in the health care system requiring specialist therapeutic and nursing knowledge. In this descriptive pilot study, we investigated the effects of a team building process on perceived work environment, self-ascribed professional competence, life satisfaction, and client satisfaction in an anthroposophic specialized hospital for neurological rehabilitation. The team-building process consisted of didactic instruction and training in problem-solving, teambuilding and constructive conflict resolution.
Methods: Seventy seven staff members and 44 patients' relatives were asked to complete a survey that included the Work Environment Scale (WES-10), a Life Satisfaction Scale (BMLSS), the Conviction of Therapeutic Competency (CTC) scale and the Client Satisfaction Questionnaire (CSQ-8). To evaluate the outcome of the team building process, we analyzed changes over time in the WES-10 subscales. Additionally the interrelationship between the WES-10 subscales with other subscales and with sociodemographic parameters like age, gender was calculated by means of a bivariate correlation analysis.
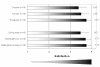
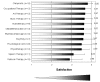
Results: The team building process had a significant positive effect on perceived work environment in only one area. There was a significant improvement in the ward staffs' perception of their ability to constructively resolve conflicts 3 years after inception of the team building process than there was before inception. However, even in a unit that utilized holistic treatment and nursing in the care of severely disable patients, such care necessitating a very heavy workload, the measurements on the Self Realization, Life Satisfaction and Conviction of Therapeutic Competency scales remained high and unchanged over the three year time period of the study.
Conclusions: Strategic interventions might be an option to improve interpersonal relationships and finally quality of patient care.
Figures
References
-
- McGowan B. Self-reported stress and its effects on nurses. Nurs Stand. 2001;15:33–38. - PubMed
-
- Melchior ME, Berg AA van den, Halfens R, Huyer Abu-Saad H, Philipsen H, Gassman P. Burnout and the work environment of nurses in psychiatric long-stay care settings. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 1997;32:158–164. - PubMed
-
- Maslch C, Jackson SE. In: Social Psychology of health and illness. Sanders G, Suls J, editor. Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum; 1982. Burnout in Health Professions: A Social Psychological Analysis; pp. 227–251.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

