Parenteral nutrition support for patients with pancreatic cancer. Results of a phase II study
- PMID: 20214798
- PMCID: PMC2841666
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-86
Parenteral nutrition support for patients with pancreatic cancer. Results of a phase II study
Abstract
Background: Cachexia is a common problem in patients (pts) suffering from upper gastrointestinal cancer. In addition, most of these patients suffer from malabsorption and stenosis of the gastrointestinal tract due to their illness. Various methods of supplementary nutrition (enteral, parenteral) are practised. In patients with advanced pancreatic cancer (APC), phase angle, determined by bio-electrical impedance analysis (BIA), seems to be a survival predictor. The positive influence of BIA determinate predictors by additional nutrition is currently under discussion.
Methods: To examine the impact of additional parenteral nutrition (APN) we assessed outpatients suffering from APC and progressive cachexia. The assessment based on the BIA method. Assessment parameters were phase angle, ECM/BCM index (ratio of extracellular mass to body cell mass), and BMI (body mass index). Patients suffering from progressive weight loss in spite of additional enteral nutritional support were eligible for the study.
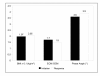
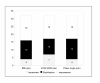
Results: Median treatment duration in 32 pts was 18 [8-35] weeks. Response evaluation showed a benefit in 27 pts (84%) in at least one parameter. 14 pts (43.7%) improved or stabilised in all three parameters. The median ECM/BCM index was 1.7 [1.11-3.14] at start of APN and improved down to 1.5 [1.12-3.36] during therapy. The median BMI increased from 19.7 [14.4-25.9] to 20.5 [15.4-25.0]. The median phase angle improved by 10% from 3.6 [2.3-5.1] to 3.9 [2.2-5.1].
Conclusions: We demonstrated the positive impact of APN on the assessed parameters, first of all the phase angle, and we observed at least a temporary benefit or stabilisation of the nutritional status in the majority of the investigated patients. Based on these findings we are currently investigating the impact of APN on survival in a larger patient cohort.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT00919659.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Parenteral nutrition support for patients with pancreatic cancer--improvement of the nutritional status and the therapeutic outcome.Anticancer Res. 2012 May;32(5):2111-8. Anticancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22593497
-
Effects of enteral nutrition and parenteral nutrition on survival in patients with advanced cancer cachexia: Analysis of a multicenter prospective cohort study.Clin Nutr. 2021 Mar;40(3):1168-1175. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2020.07.027. Epub 2020 Jul 31. Clin Nutr. 2021. PMID: 32771283
-
Feasibility and efficacy of enteral tube feeding on weight stability, lean body mass, and patient-reported outcomes in pancreatic cancer cachexia.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2021 Dec;12(6):1959-1968. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12799. Epub 2021 Oct 5. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2021. PMID: 34609081 Free PMC article.
-
Is there a role for parenteral nutrition or hydration at the end of life?Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 2012 Sep;6(3):365-70. doi: 10.1097/SPC.0b013e328356ab4a. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 2012. PMID: 22801468 Review.
-
The value of bioelectrical impedance analysis and phase angle in the evaluation of malnutrition and quality of life in cancer patients--a comprehensive review.Eur J Clin Nutr. 2015 Dec;69(12):1290-7. doi: 10.1038/ejcn.2015.126. Epub 2015 Jul 29. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2015. PMID: 26220573 Review.
Cited by
-
L-Carnitine-supplementation in advanced pancreatic cancer (CARPAN)--a randomized multicentre trial.Nutr J. 2012 Jul 23;11:52. doi: 10.1186/1475-2891-11-52. Nutr J. 2012. PMID: 22824168 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pancreas Cancer-Associated Weight Loss.Oncologist. 2019 May;24(5):691-701. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0266. Epub 2018 Dec 27. Oncologist. 2019. PMID: 30591550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-protein home parenteral nutrition in malnourished oncology patients: a systematic literature review.Support Care Cancer. 2023 Dec 22;32(1):52. doi: 10.1007/s00520-023-08218-z. Support Care Cancer. 2023. PMID: 38129578 Free PMC article.
-
Nutrition in Pancreatic Diseases: A Roadmap for the Gastroenterologist.GE Port J Gastroenterol. 2023 Jul 12;31(1):1-13. doi: 10.1159/000530835. eCollection 2024 Feb. GE Port J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 38314032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gastrointestinal Cancer Patient Nutritional Management: From Specific Needs to Novel Epigenetic Dietary Approaches.Nutrients. 2022 Apr 8;14(8):1542. doi: 10.3390/nu14081542. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35458104 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pelzer U. Second-line chemotherapy in advanced pancreatic cancer. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2008;177:61–64. full_text. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous