Different stress-related phenotypes of BALB/c mice from in-house or vendor: alterations of the sympathetic and HPA axis responsiveness
- PMID: 20214799
- PMCID: PMC2845127
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6793-10-2
Different stress-related phenotypes of BALB/c mice from in-house or vendor: alterations of the sympathetic and HPA axis responsiveness
Abstract
Background: Laboratory routine procedures such as handling, injection, gavage or transportation are stressful events which may influence physiological parameters of laboratory animals and may interfere with the interpretation of the experimental results. Here, we investigated if female BALB/c mice derived from in-house breeding and BALB/c mice from a vendor which were shipped during their juvenile life differ in their HPA axis activity and stress responsiveness in adulthood.
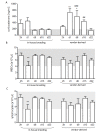
Results: We show that already transferring the home cage to another room is a stressful event which causes an increased HPA axis activation for at least 24 hours as well as a loss of circulating lymphocytes which normalizes during a few days after transportation. However and important for the interpretation of experimental data, commercially available strain-, age- and gender-matched animals that were shipped over-night showed elevated glucocorticoid levels for up to three weeks after shipment, indicating a heightened HPA axis activation and they gained less body weight during adolescence. Four weeks after shipment, these vendor-derived mice showed increased corticosterone levels at 45-min after intraperitoneal ACTH challenge but, unexpectedly, no acute stress-induced glucocorticoid release. Surprisingly, activation of monoaminergic pathways were identified to inhibit the central nervous HPA axis activation in the vendor-derived, shipped animals since depletion of monoamines by reserpine treatment could restore the stress-induced HPA axis response during acute stress.
Conclusions: In-house bred and vendor-derived BALB/c mice show a different stress-induced HPA axis response in adulthood which seems to be associated with different central monoaminergic pathway activity. The stress of shipment itself and/or differences in raising conditions, therefore, can cause the development of different stress response phenotypes which needs to be taken into account when interpreting experimental data.
Figures
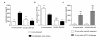

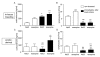
Similar articles
-
A chronic combinatory stress model that activates the HPA axis and avoids habituation in BALB/C mice.J Neurosci Methods. 2013 Feb 15;213(1):70-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2012.10.015. Epub 2012 Dec 1. J Neurosci Methods. 2013. PMID: 23206838
-
Repeated stress alters the ability of nicotine to activate the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis.J Neurochem. 2006 Dec;99(5):1321-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04217.x. Epub 2006 Oct 25. J Neurochem. 2006. PMID: 17064351
-
Functional characterization of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis of the Wistar Audiogenic Rat (WAR) strain.Brain Res. 2011 Mar 24;1381:141-7. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2011.01.042. Epub 2011 Jan 21. Brain Res. 2011. PMID: 21256829
-
Social stress adapts signaling pathways involved in stimulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis.J Physiol Pharmacol. 1999 Sep;50(3):367-79. J Physiol Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10574467 Review.
-
Investigations of HPA function and the enduring consequences of stressors in adolescence in animal models.Brain Cogn. 2010 Feb;72(1):73-85. doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2009.06.003. Epub 2009 Jul 17. Brain Cogn. 2010. PMID: 19616355 Review.
Cited by
-
Sex Differences in Physiological Acclimatization after Transfer in Wistar Rats.Animals (Basel). 2014 Oct 30;4(4):693-711. doi: 10.3390/ani4040693. Animals (Basel). 2014. PMID: 26479007 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Ground Transportation on Adrenocortical Activity in Prepuberal Female Mice from Five Different Genetic Backgrounds.Animals (Basel). 2019 May 15;9(5):239. doi: 10.3390/ani9050239. Animals (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31096568 Free PMC article.
-
Indirect sympatholytic actions at β-adrenoceptors account for the ocular hypotensive actions of cannabinoid receptor agonists.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011 Dec;339(3):757-67. doi: 10.1124/jpet.111.185769. Epub 2011 Sep 1. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011. PMID: 21885619 Free PMC article.
-
Paternal Preconception Chronic Variable Stress Confers Attenuated Ethanol Drinking Behavior Selectively to Male Offspring in a Pre-Stress Environment Dependent Manner.Front Behav Neurosci. 2018 Nov 2;12:257. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2018.00257. eCollection 2018. Front Behav Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30450042 Free PMC article.
-
Exposure to a firefighting overhaul environment without respiratory protection increases immune dysregulation and lung disease risk.PLoS One. 2018 Aug 21;13(8):e0201830. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201830. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30130361 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balcombe JP, Barnard ND, Sandusky C. Laboratory routines cause animal stress. Contemporary Topics in Laboratory Animal Science. 2004;43(6):42–51. - PubMed
-
- Besch EL, Chou BJ. Physiological responses to blood collection methods in rats. Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine. 1971;138(3):1019. - PubMed
-
- Brown AP, Dinger N, Levine BS. Stress produced by gavage administration in the rat. Contemporary Topics in Laboratory Animal Science. 2000;39(1):17–21. - PubMed

