The Puf family of RNA-binding proteins in plants: phylogeny, structural modeling, activity and subcellular localization
- PMID: 20214804
- PMCID: PMC2848763
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-44
The Puf family of RNA-binding proteins in plants: phylogeny, structural modeling, activity and subcellular localization
Abstract
Background: Puf proteins have important roles in controlling gene expression at the post-transcriptional level by promoting RNA decay and repressing translation. The Pumilio homology domain (PUM-HD) is a conserved region within Puf proteins that binds to RNA with sequence specificity. Although Puf proteins have been well characterized in animal and fungal systems, little is known about the structural and functional characteristics of Puf-like proteins in plants.
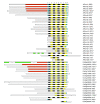
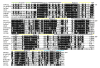
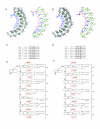
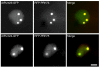
Results: The Arabidopsis and rice genomes code for 26 and 19 Puf-like proteins, respectively, each possessing eight or fewer Puf repeats in their PUM-HD. Key amino acids in the PUM-HD of several of these proteins are conserved with those of animal and fungal homologs, whereas other plant Puf proteins demonstrate extensive variability in these amino acids. Three-dimensional modeling revealed that the predicted structure of this domain in plant Puf proteins provides a suitable surface for binding RNA. Electrophoretic gel mobility shift experiments showed that the Arabidopsis AtPum2 PUM-HD binds with high affinity to BoxB of the Drosophila Nanos Response Element I (NRE1) RNA, whereas a point mutation in the core of the NRE1 resulted in a significant reduction in binding affinity. Transient expression of several of the Arabidopsis Puf proteins as fluorescent protein fusions revealed a dynamic, punctate cytoplasmic pattern of localization for most of these proteins. The presence of predicted nuclear export signals and accumulation of AtPuf proteins in the nucleus after treatment of cells with leptomycin B demonstrated that shuttling of these proteins between the cytosol and nucleus is common among these proteins. In addition to the cytoplasmically enriched AtPum proteins, two AtPum proteins showed nuclear targeting with enrichment in the nucleolus.
Conclusions: The Puf family of RNA-binding proteins in plants consists of a greater number of members than any other model species studied to date. This, along with the amino acid variability observed within their PUM-HDs, suggests that these proteins may be involved in a wide range of post-transcriptional regulatory events that are important in providing plants with the ability to respond rapidly to changes in environmental conditions and throughout development.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Molecular characterization of Arabidopsis thaliana PUF proteins--binding specificity and target candidates.FEBS J. 2009 Oct;276(19):5456-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07230.x. Epub 2009 Aug 13. FEBS J. 2009. PMID: 19682068
-
Functional dissection of the plant-specific SBP-domain: overlap of the DNA-binding and nuclear localization domains.J Mol Biol. 2005 Sep 23;352(3):585-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2005.07.013. J Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 16095614
-
Genome-wide comparative phylogenetic analysis of the rice and Arabidopsis Dof gene families.BMC Evol Biol. 2003 Jul 23;3:17. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-3-17. Epub 2003 Jul 23. BMC Evol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12877745 Free PMC article.
-
Pumilio Puf domain RNA-binding proteins in Arabidopsis.Plant Signal Behav. 2011 Mar;6(3):364-8. doi: 10.4161/psb.6.3.14380. Epub 2011 Mar 1. Plant Signal Behav. 2011. PMID: 21350339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The PUF family of RNA-binding proteins: does evolutionarily conserved structure equal conserved function?IUBMB Life. 2003 Jul;55(7):359-66. doi: 10.1080/15216540310001603093. IUBMB Life. 2003. PMID: 14584586 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging Roles of RNA-Binding Proteins in Seed Development and Performance.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 17;21(18):6822. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186822. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32957608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural basis for the specific recognition of 18S rRNA by APUM23.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Nov 16;45(20):12005-12014. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx872. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 29036323 Free PMC article.
-
The Regulatory Roles of RNA-Binding Proteins in Plant Salt Stress Response.Plants (Basel). 2025 May 7;14(9):1402. doi: 10.3390/plants14091402. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40364430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Puf4 -mediated oxidative stress virulence attenuation in Cryptococcus neoformans.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Aug 11;15:1628448. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1628448. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40861481 Free PMC article.
-
A diagnostic marker kit for Fusarium wilt and sterility mosaic diseases resistance in pigeonpea.Theor Appl Genet. 2021 Jan;134(1):367-379. doi: 10.1007/s00122-020-03702-0. Epub 2020 Oct 20. Theor Appl Genet. 2021. PMID: 33079215 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lehmann R, Nusslein-Volhard C. Involvement of the pumilio gene in the transport of an abdominal signal in the Drosophila embryo. Nature. 1987;329:167–170. doi: 10.1038/329167a0. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

