Cell cycle arrest by a gradient of Dpp signaling during Drosophila eye development
- PMID: 20214806
- PMCID: PMC2846880
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-213X-10-28
Cell cycle arrest by a gradient of Dpp signaling during Drosophila eye development
Abstract
Background: The secreted morphogen Dpp plays important roles in spatial regulation of gene expression and cell cycle progression in the developing Drosophila eye. Dpp signaling is required for timely cell cycle arrest ahead of the morphogenetic furrow as a prelude to differentiation, and is also important for eye disc growth. The dpp gene is expressed at multiple locations in the eye imaginal disc, including the morphogenetic furrow that sweeps across the eye disc as differentiation initiates.
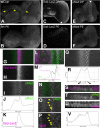
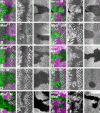
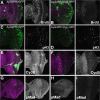
Results: Studies of Brinker and Dad expression, and of Mad phosphorylation, establish that there is a gradient of Dpp signaling in the eye imaginal disc anterior to the morphogenetic furrow, predominantly in the anterior-posterior axis, and also Dpp signaling at the margins of the disc epithelium and in the dorsal peripodial membrane. Almost all signaling activity seems to spread through the plane of the epithelia, although peripodial epithelium cells can also respond to underlying disc cells. There is a graded requirement for Dpp signaling components for G1 arrest in the eye disc, with more stringent requirements further anteriorly where signaling is lower. The signaling level defines the cell cycle response, because elevated signaling through expression of an activated Thickveins receptor molecule arrested cells at more anterior locations. Very anterior regions of the eye disc were not arrested in response to activated receptor, however, and evidence is presented that expression of the Homothorax protein may contribute to this protection. By contrast to activated Thickveins, ectopic expression of processed Dpp leads to very high levels of Mad phosphorylation which appear to have non-physiological consequences.
Conclusions: G1 arrest occurs at a threshold level of Dpp signaling within a morphogen gradient in the anterior eye. G1 arrest is specific for one competent domain in the eye disc, allowing Dpp signaling to promote growth at earlier developmental stages.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hedgehog and Dpp signaling induce cadherin Cad86C expression in the morphogenetic furrow during Drosophila eye development.Mech Dev. 2008 Aug;125(8):712-28. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2008.04.005. Epub 2008 Apr 27. Mech Dev. 2008. PMID: 18539010
-
Growth control by a moving morphogen gradient during Drosophila eye development.Development. 2014 May;141(9):1884-93. doi: 10.1242/dev.105650. Development. 2014. PMID: 24757005
-
decapentaplegic is required for arrest in G1 phase during Drosophila eye development.Development. 1998 Dec;125(24):5069-78. doi: 10.1242/dev.125.24.5069. Development. 1998. PMID: 9811590
-
Jun N-terminal kinase signaling makes a face.Fly (Austin). 2016 Oct;10(4):195-203. doi: 10.1080/19336934.2016.1207012. Epub 2016 Jul 6. Fly (Austin). 2016. PMID: 27384866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The missing link: implementation of morphogenetic growth control on the cellular and molecular level.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2011 Dec;21(6):690-5. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2011.09.002. Epub 2011 Sep 28. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2011. PMID: 21959321 Review.
Cited by
-
Rare EIF4A2 variants are associated with a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by intellectual disability, hypotonia, and epilepsy.Am J Hum Genet. 2023 Jan 5;110(1):120-145. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2022.11.011. Epub 2022 Dec 16. Am J Hum Genet. 2023. PMID: 36528028 Free PMC article.
-
Retinal determination genes function along with cell-cell signals to regulate Drosophila eye development: examples of multi-layered regulation by master regulators.Bioessays. 2011 Jul;33(7):538-46. doi: 10.1002/bies.201000131. Epub 2011 May 24. Bioessays. 2011. PMID: 21607995 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between sex determination cascade and major signaling pathways during Drosophila eye development: Perspectives for future research.Dev Biol. 2021 Aug;476:41-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2021.03.005. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33745943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quiescence: early evolutionary origins and universality do not imply uniformity.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2011 Dec 27;366(1584):3498-507. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2011.0079. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2011. PMID: 22084377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TGF-β Family Signaling in Drosophila.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2017 Sep 1;9(9):a022152. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a022152. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2017. PMID: 28130362 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

