Worksite interventions for preventing physical deterioration among employees in job-groups with high physical work demands: background, design and conceptual model of FINALE
- PMID: 20214807
- PMCID: PMC2841104
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-10-120
Worksite interventions for preventing physical deterioration among employees in job-groups with high physical work demands: background, design and conceptual model of FINALE
Abstract
Background: A mismatch between individual physical capacities and physical work demands enhance the risk for musculoskeletal disorders, poor work ability and sickness absence, termed physical deterioration. However, effective intervention strategies for preventing physical deterioration in job groups with high physical demands remains to be established. This paper describes the background, design and conceptual model of the FINALE programme, a framework for health promoting interventions at 4 Danish job groups (i.e. cleaners, health-care workers, construction workers and industrial workers) characterized by high physical work demands, musculoskeletal disorders, poor work ability and sickness absence.
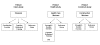
Methods/design: A novel approach of the FINALE programme is that the interventions, i.e. 3 randomized controlled trials (RCT) and 1 exploratory case-control study are tailored to the physical work demands, physical capacities and health profile of workers in each job-group. The RCT among cleaners, characterized by repetitive work tasks and musculoskeletal disorders, aims at making the cleaners less susceptible to musculoskeletal disorders by physical coordination training or cognitive behavioral theory based training (CBTr). Because health-care workers are reported to have high prevalence of overweight and heavy lifts, the aim of the RCT is long-term weight-loss by combined physical exercise training, CBTr and diet. Construction work, characterized by heavy lifting, pushing and pulling, the RCT aims at improving physical capacity and promoting musculoskeletal and cardiovascular health. At the industrial work-place characterized by repetitive work tasks, the intervention aims at reducing physical exertion and musculoskeletal disorders by combined physical exercise training, CBTr and participatory ergonomics. The overall aim of the FINALE programme is to improve the safety margin between individual resources (i.e. physical capacities, and cognitive and behavioral skills) and physical work demands, and thereby reduce the physical deterioration in a long term perspective by interventions tailored for each respective job-group.
Discussion: The FINALE programme has the potential to provide evidence-based knowledge of significant importance for public health policy and health promotion strategies for employees at high risk for physical deterioration.
Trial registrations: ISRCTN96241850, NCT01015716 and NCT01007669.
Figures
References
-
- Ilmarinen J. Work ability - a comprehensive concept for occupational health research and prevention. Scandinavian Journal of Work Environment & Health. 2009;10:1–5. - PubMed
-
- Tuomi K, Ilmarinen J, Seitsamo J, Huuhtanen P, Martikainen R, Nygard CH, Klockars M. Summary of the Finnish research project (1981-1992) to promote the health and work ability of aging workers. Scandinavian Journal of Work Environment & Health. 1997;10:66–71. - PubMed
-
- Hasselhorn H-M, Tackenberg P, Müller BH. Working Conditions and intent to leave the profession among nursing staff in Europe. University of Wuppertal; 2007.
-
- Tuomi K, Ilmarinen J, Eskelinen L, Jarvinen E, Toikkanen J, Klockars M. Prevalence and incidence rates of diseases and work ability in different work categories of municipal occupations. Scandinavian Journal of Work Environment & Health. 1991;10:67–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical