Characterization of the expression and regulation of MK5 in the murine ventricular myocardium
- PMID: 20214976
- PMCID: PMC3415464
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.02.009
Characterization of the expression and regulation of MK5 in the murine ventricular myocardium
Abstract
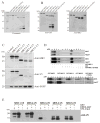
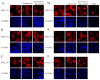
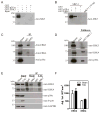
MK5, a member of the MAPK-activated protein kinase family, is highly expressed in the heart. Whereas MK2 and MK3 are activated by p38 MAPK, MK5 has also been shown to be activated by ERK3 and ERK4. We studied the regulation of MK5 in mouse heart. mRNA for 5 splice variants (MK5.1-5.5), including the original form (MK5.1), was detected. MK5 comprises 14 exons: exon 12 splicing was modified in MK5.2, MK5.3, and MK5.5. MK5.2 and MK5.5 lacked 6 bases at the 3'-end of exon 12, whereas MK5.3 lacked exon 12, resulting in a frame shift and premature termination of translation at codon 3 of exon 13. MK5.4 and MK5.5 lacked exons 2-6, encoding kinase subdomains I-VI, and were kinase-dead. All 5 MK5 variants were detected at the mRNA level in all mouse tissues examined; however, their relative abundance was tissue-specific. Furthermore, the relative abundance of variant mRNA was altered both during hypertrophy and postnatal cardiac development, suggesting that the generation or the stability of MK5 variant mRNAs is subject to regulation. When expressed in HEK293 cells, MK5.1, MK5.2 and MK5.3 were nuclear whereas MK5.4 and MK5.5 were cytoplasmic. A p38 MAPK activator, anisomycin, induced the redistribution of each variant. In contrast, MK5 co-immunoprecipitated ERK3, but not ERK4 or p38 alpha, in control and hypertrophying hearts. GST pull-down assays revealed unbound ERK4 and p38 alpha but no free MK5 or ERK3 in heart lysates. Hence, 1) in heart MK5 complexes with ERK3 and 2) MK5 splice variants may mediate distinct effects thus increasing the functional diversity of ERK3-MK5 signaling.
(c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
MK5: A novel regulator of cardiac fibroblast function?IUBMB Life. 2017 Oct;69(10):785-794. doi: 10.1002/iub.1677. Epub 2017 Sep 11. IUBMB Life. 2017. PMID: 28941148 Review.
-
Characterization of the atypical MAPK ERK4 and its activation of the MAPK-activated protein kinase MK5.J Biol Chem. 2006 Nov 17;281(46):35511-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M606693200. Epub 2006 Sep 13. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16973613
-
Docking of PRAK/MK5 to the atypical MAPKs ERK3 and ERK4 defines a novel MAPK interaction motif.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jul 17;284(29):19392-401. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.023283. Epub 2009 May 27. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19473979 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of a novel MK3 splice variant from murine ventricular myocardium.Cell Signal. 2010 Oct;22(10):1502-12. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.05.019. Epub 2010 Jun 4. Cell Signal. 2010. PMID: 20570725 Free PMC article.
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 and MK2, MK3 and MK5: ménage à trois or ménage à quatre?Cell Signal. 2010 Aug;22(8):1185-92. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.03.002. Epub 2010 Mar 11. Cell Signal. 2010. PMID: 20227494 Review.
Cited by
-
MK5 haplodeficiency decreases collagen deposition and scar size during post-myocardial infarction wound repair.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019 Jun 1;316(6):H1281-H1296. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00532.2017. Epub 2019 Mar 22. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30901279 Free PMC article.
-
Activation and function of the MAPKs and their substrates, the MAPK-activated protein kinases.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2011 Mar;75(1):50-83. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00031-10. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21372320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of hsp27 kinases activated by elevated aortic pressure in heart.Mol Cell Biochem. 2012 Dec;371(1-2):31-42. doi: 10.1007/s11010-012-1420-x. Epub 2012 Aug 10. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22878564 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of Two Gene-Targeting Approaches Challenges the Tumor-Suppressive Role of the Protein Kinase MK5/PRAK.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 21;10(8):e0136138. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136138. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26295581 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac Fibroblast p38 MAPK: A Critical Regulator of Myocardial Remodeling.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2019 Aug 7;6(3):27. doi: 10.3390/jcdd6030027. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2019. PMID: 31394846 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen Z, Gibson TB, Robinson F, Silvestro L, Pearson G, Xu B, Wright A, Vanderbilt C, Cobb MH. Chem Rev. 2001;101(8):2449–2476. - PubMed
-
- Kotlyarov A, Neininger A, Schubert C, Eckert R, Birchmeier C, Volk H-D, Gaestel M. Nature Cell Biol. 1999;1:94–97. - PubMed
-
- Gaestel M. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7(2):120–130. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

