The RNA-binding protein bicaudal C regulates polycystin 2 in the kidney by antagonizing miR-17 activity
- PMID: 20215348
- PMCID: PMC2835326
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.046045
The RNA-binding protein bicaudal C regulates polycystin 2 in the kidney by antagonizing miR-17 activity
Abstract
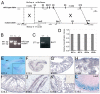
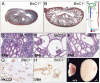
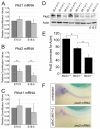
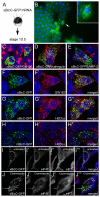
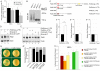
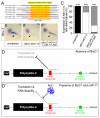
The RNA-binding protein Bicaudal C is an important regulator of embryonic development in C. elegans, Drosophila and Xenopus. In mouse, bicaudal C (Bicc1) mutants are characterized by the formation of fluid-filled cysts in the kidney and by expansion of epithelial ducts in liver and pancreas. This phenotype is reminiscent of human forms of polycystic kidney disease (PKD). Here, we now provide data that Bicc1 functions by modulating the expression of polycystin 2 (Pkd2), a member of the transient receptor potential (TRP) superfamily. Molecular analyses demonstrate that Bicc1 acts as a post-transcriptional regulator upstream of Pkd2. It regulates the stability of Pkd2 mRNA and its translation efficiency. Bicc1 antagonized the repressive activity of the miR-17 microRNA family on the 3'UTR of Pkd2 mRNA. This was substantiated in Xenopus, in which the pronephric defects of bicc1 knockdowns were rescued by reducing miR-17 activity. At the cellular level, Bicc1 protein is localized to cytoplasmic foci that are positive for the P-body markers GW182 and HEDLs. Based on these data, we propose that the kidney phenotype in Bicc1(-/-) mutant mice is caused by dysregulation of a microRNA-based translational control mechanism.
Figures

References
-
- Anderson P., Kedersha N. (2008). Stress granules: the Tao of RNA triage. Trends Biochem. Sci. 33, 141-150 - PubMed
-
- Blum M., Andre P., Muders K., Schweickert A., Fischer A., Bitzer E., Bogusch S., Beyer T., van Straaten H. W., Viebahn C. (2007). Ciliation and gene expression distinguish between node and posterior notochord in the mammalian embryo. Differentiation 75, 133-146 - PubMed
-
- Burn T. C., Connors T. D., Dackowski W. R., Petry L. R., Van Raay T. J., Millholland J. M., Venet M., Miller G., Hakim R. M., Landes G. M., et al. (1995). Analysis of the genomic sequence for the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (PKD1) gene predicts the presence of a leucine-rich repeat. The American PKD1 Consortium (APKD1 Consortium). Hum. Mol. Genet. 4, 575-582 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

